-
. Theory and Methods of Visual Inspection with Image Sequences. Wuhan University Press, ISBN: 978-7-307-06654-0, 148P, 2008.12.
- All
- All
- English Journal
- Chinese Journal
-
, Zhi Zheng, Yimin Luo, Yanfeng Zhang, Yi Wan, Jun Wu, Zhiyong Peng, Xiu Liu. (2019) A CNN-Based Subpixel Level DSM Generation Approach via Single Image Super-Resolution. In: Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, Vol.85(10):51-491.
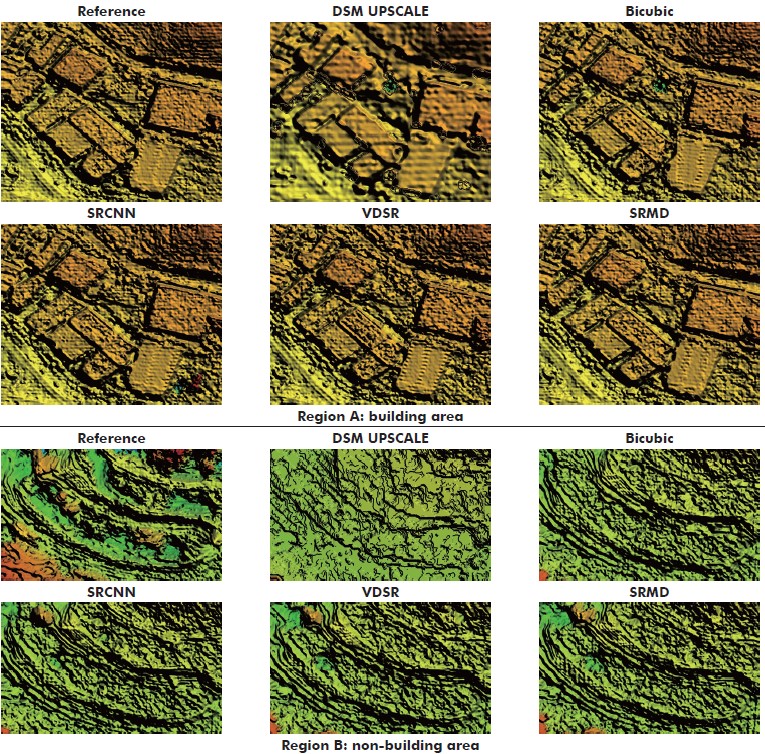
Abstract: Previous work for subpixel level Digital Surface Model (DSM) generation mainly focused on data fusion techniques, which are extremely limied by the difficulty of multisource data acquisition. Although several DSMsuper resolution (SR) methods have been developed to ease the problem, a new issue that plenty of DSM samples are needed to train the model is raised. Therefore, considering the original images have vital influence on its DSM's accuracy, we address the problem by directly improving images resolution. Several SR models are refined and brought into the traditional DSMgeneration process as an image quality improvement stage to construct an easy but effective workflow for subpixel level DSM generation. Experiments verified the validity and significance of bringing SR technology into this kind of application. Statistical analysis also confirmed that a subpixel level DSM with higher fidelity can be obtained more easily compared to directly DSM interpolation. [full text] [link]
-
Xiaohu Yan, Fazhi He, , Xunwei Xie. (2019) An optimizer ensemble algorithm and its application to image registration. In: Integrated Computer Aided Engineering, Vol.26(1):1-17.

Abstract: The design of effective optimization algorithms is always a hot research topic. An optimizer ensemble where any population-based optimization algorithm can be integrated is proposed in this study. First, the optimizer ensemble framework based on ensemble learning is presented. The learning table consisting of the population members of all optimizers is constructed to share information. The maximum number of iterations is divided into several exchange iterations. Each optimizer exchanges individuals with the learning table in exchange iterations and runs independently in the other iterations. Exchange individuals are generated by a bootstrap sample from the learning table. To maintain a balance between exchange individuals and preserved individuals, the exchange number of each optimizer is adaptively assigned according to its fitness. The output is obtained by the voting approach that selects the highest ranked solution. Second, an optimizer ensemble algorithm (OEA) which combines multiple population-based optimization algorithms is proposed. The computational complexity, convergence, and diversity of OEA are analyzed. Finally, extensive experiments on benchmark functions demonstrate that OEA outperforms several state-of-the-art algorithms. OEA is used to search the maximum mutual information in image registration. The high performance of OEA is further verified by a large number of registration results on real remote sensing images. [full text] [link]
-
Bin Zhang, , Shugen Wang. (2019) A Lightweight and Discriminative Model for Remote Sensing Scene Classification With Multidilation Pooling Module. In: IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, Vol.12(8):2636-2653.
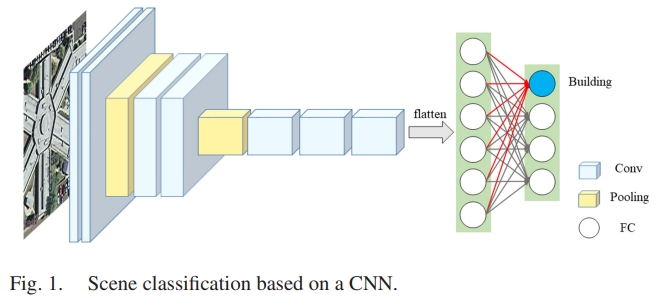
Abstract: With the growing spatial resolution of satellite images, high spatial resolution (HSR) remote sensing imagery scene classification has become a challenging task due to the highly complex geometrical structures and spatial patterns in HSR imagery. The key issue in scene classification is how to understand the semantic content of the images effectively, and researchers have been looking for ways to improve the process. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs), which have achieved amazing results in natural image classification, were introduced for remote sensing image scene classification. Most of the researches to date have improved the final classification accuracy by merging the features of CNNs. However, the entire models become relatively complex and cannot extract more effective features. To solve this problem, in this paper, we propose a lightweight and effective CNN which is capable of maintaining high accuracy. We use MobileNet V2 as a base network and introduce the dilated convolution and channel attention to extract discriminative features. To improve the performance of the CNN further, we also propose a multidilation pooling module to extract multiscale features. Experiments are performed on six datasets, and the results verify that our method can achieve higher accuracy compared to the current state-of-the-art methods. [full text] [link]
-
Daifeng Peng, , Haiyan Guan (2019) End-to-End Change Detection for High Resolution Satellite Images Using Improved UNet++. In: Remote Sensing, 11:1382.
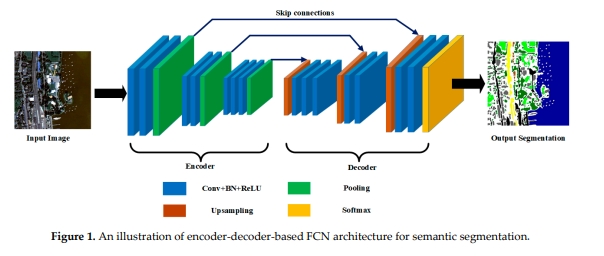
Abstract: Change detection (CD) is essential to the accurate understanding of land surface changes using available Earth observation data. Due to the great advantages in deep feature representation and nonlinear problem modeling, deep learning is becoming increasingly popular to solve CD tasks in remote-sensing community. However, most existing deep learning-based CD methods are implemented by either generating difference images using deep features or learning change relations between pixel patches, which leads to error accumulation problems since many intermediate processing steps are needed to obtain final change maps. To address the abovementioned issues, a novel end-to-end CD method is proposed based on an effective encoderdecoder architecture for semantic segmentation named UNet++, where change maps could be learned from scratch using available annotated datasets. Firstly, co-registered image pairs are concatenated as an input for the improved UNet++ network, where both global and fine-grained information can be utilized to generate feature maps with high spatial accuracy. Then, the fusion strategy of multiple side outputs is adopted to combine change maps from different semantic levels, thereby generating a final change map with high accuracy. The effectiveness and reliability of our proposed CD method are verified on very-high-resolution (VHR) satellite image datasets. Extensive experimental results have shown that our proposed approach outperforms the other state-of-the-art CD methods. [full text] [link]
-
Xinyi Liu, , Xiao Ling, Yi Wan, Linyu Liu, Qian Li. (2019) TopoLAP: Topology Recovery for Building Reconstruction by Deducing the Relationships between Linear and Planar Primitives. In: Remote Sensing, Vol.11:1372.
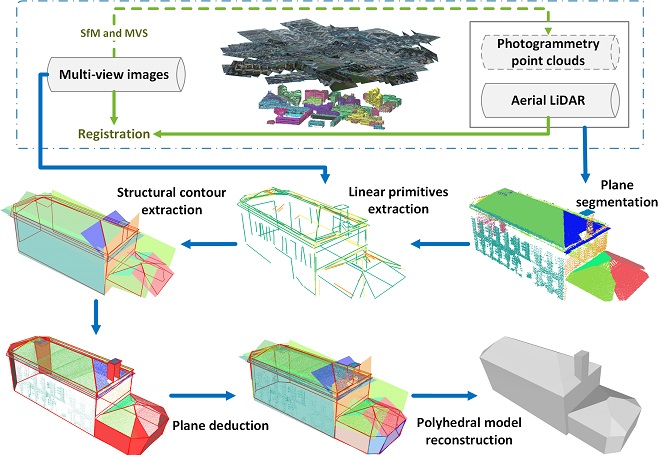
Abstract: Limited by the noise, missing data and varying sampling density of the point clouds, planar primitives are prone to be lost during plane segmentation, leading to topology errors when reconstructing complex building models. In this paper, a pipeline to recover the broken topology of planar primitives (TopoLAP) is proposed to reconstruct level of details 3 (LoD3) models. Firstly, planar primitives are segmented from the incomplete point clouds and feature lines are detected both from point clouds and images. Secondly, the structural contours of each plane segment are reconstructed by subset selection from intersections of these feature lines. Subsequently, missing planes are recovered by plane deduction according to the relationships between linear and planar primitives. Finally, the manifold and watertight polyhedral building models are reconstructed based on the optimized PolyFit framework. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed pipeline can handle partial incomplete point clouds and reconstruct the LoD3 models of complex buildings automatically. A comparative analysis indicates that the proposed method performs better to preserve sharp edges and achieves a higher fitness and correction rate than rooftop-based modeling and the original PolyFit algorithm. [full text] [link]
-
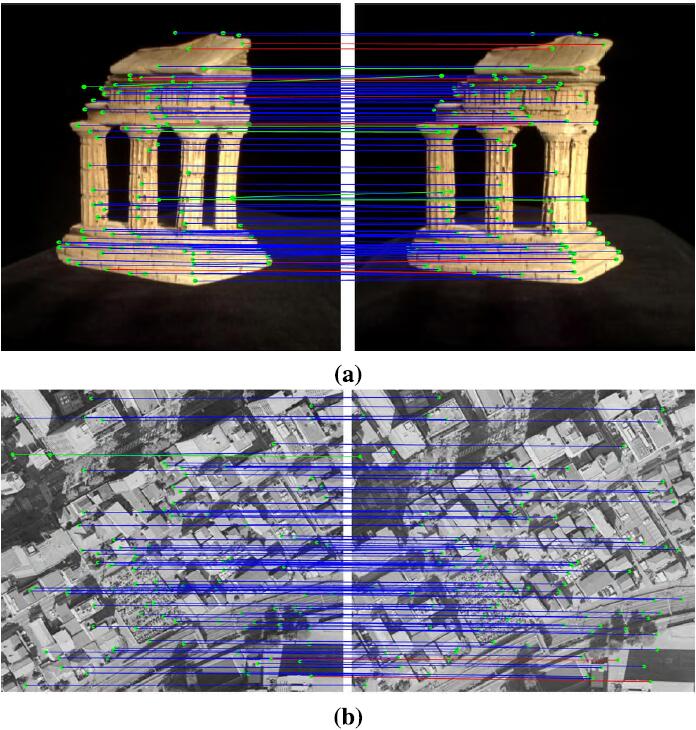
Yi Wan, , Xinyi Liu. (2019) An a-contrario method of mismatch detection for two-view pushbroom satellite images. In: ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, Vol.99:1-15.
Abstract: Mismatch detection is a key step in the geometric correction of satellite images. However, most RANSAC-based mismatch detection methods face two problems in practical application, i.e., how to preset the threshold when the apriori matching accuracy is not known and how to validate the correctness of the results when the proportions of true matches are very low. In this paper, we propose an a-contrario method named ORSA-SAT to remove the mismatches for two-view satellite images by finding the most meaningful set of matches. The formula first is defined to compute the geometric rigidity of a set of point matches according to the image match search area with the matching accuracy measured by the maximum point-to-epipolar-line distance. Then, the meaningfulness of a set is rated by a probabilistic criterion that estimates the number of false alarms (NFA), which indicates the expected times that a set can be found by chance from non-rigid and randomly distributed matched points. The criterion is a function of the quantity of point-matches and the geometric rigidity and is used in ORSA-SAT for comparing two sets. The true matches are collected by finding the most meaningful set; thus, no preset thresholds are needed to separate the true matches and the mismatches. Furthermore, the criterion also justifies the correctness of the sets obtained by ORSA-SAT since rigid sets rarely occur from mismatches. In this paper, we use both simulated data and real matched points on images captured by IKONOS-2, ZY-3, and Landsat-8 to demonstrate ORSA-SAT. The results of the simulated experiments show that both the precisions and the recalls were ensured above 80% in the correct results of ORSA-SAT even though there were over 90% mismatches originally. [full text] [link]
-
, Xinyi Liu, Yi Zhang, Xiao Ling, Xu Huang. (2019) Automatic and Unsupervised Water Body Extraction Based on Spectral-Spatial Features Using GF-1 Satellite Imagery. In: IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, Vol.16, No.6:927-931.
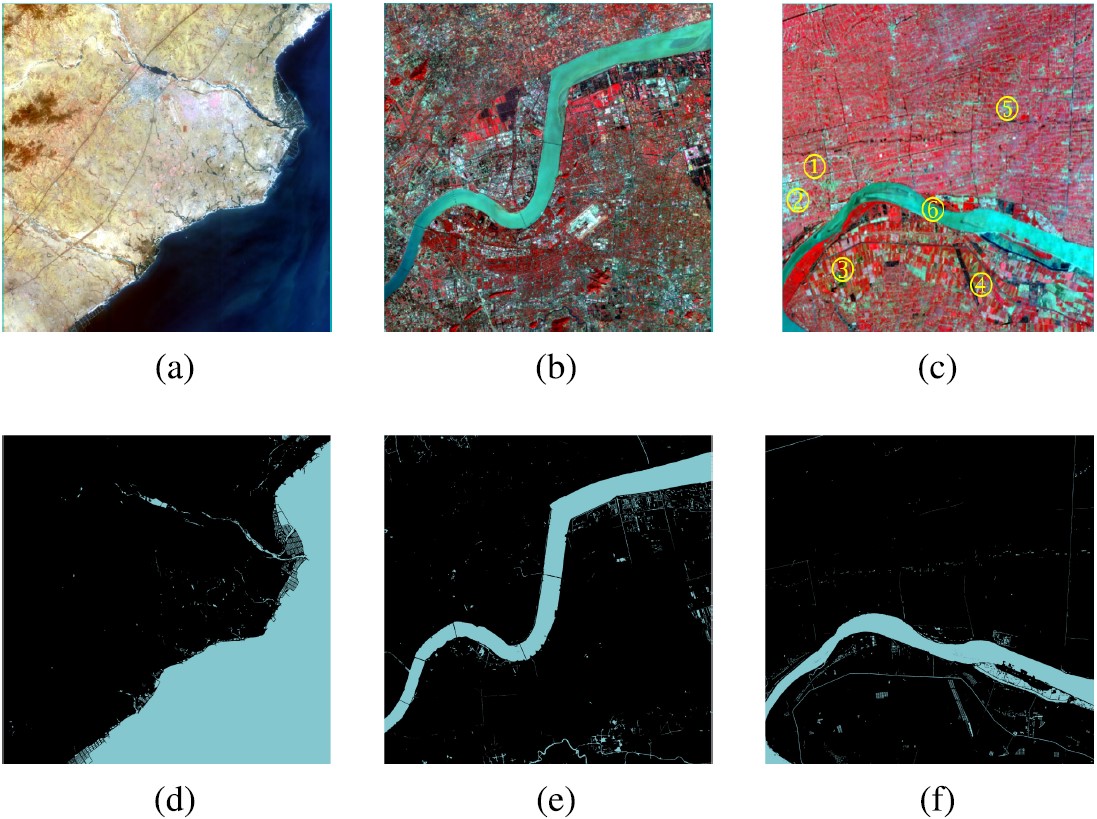

Abstract: Water body extraction from remote sensing imagery is an essential and nontrivial issue due to the complexity of the spectral characteristics of various kinds of water bodies and the redundant background information. An automatic multifeature water body extraction (MFWE) method integrating spectral and spatial features is proposed in this letter for water body extraction from GF-1 multispectral imagery in an unsupervised way. This letter first discusses a spatial feature index, called the pixel region index (PRI), to describe the smoothness in a local area surrounding a pixel. PRI is advantageous for assisting the normalized difference water index (NDWI) in detecting major water bodies, especially in urban areas. On the other hand, part of the water pixels near the borders may not be included in major water bodies, k-means clustering is subsequently conducted to cluster all the water pixels into the same group as a guide map. Finally, the major water bodies and the guide map are merged to obtain the final water mask. Our experimental results demonstrate that accurate water masks were achieved for all seven GF-1 imagery scenes examined. Three images with a complex background and water conditions were used to quantitatively compare the proposed method to NDWI thresholding and support vector machine classification, which verified the higher accuracy and effectiveness of the proposed method. [full text] [link]
-
Shunping Ji, Yanyun Shen, Meng Lu, . (2019) Building Instance Change Detection from Large-Scale Aerial Images using Convolutional Neural Networks and Simulated Samples. In: Remote Sensing, Vol.11(11):1343.

Abstract: We present a novel convolutional neural network (CNN)-based change detection framework for locating changed building instances as well as changed building pixels from very high resolution (VHR) aerial images. The distinctive advantage of the framework is the self-training ability, which is highly important in deep-learning-based change detection in practice, as high-quality samples of changes are always lacking for training a successful deep learning model. The framework consists two parts: a building extraction network to produce a binary building map and a building change detection network to produce a building change map. The building extraction network is implemented with two widely used structures: a Mask R-CNN for object-based instance segmentation, and a multi-scale full convolutional network for pixel-based semantic segmentation. The building change detection network takes bi-temporal building maps produced from the building extraction network as input and outputs a building change map at the object and pixel levels. By simulating arbitrary building changes and various building parallaxes in the binary building map, the building change detection network is well trained without real-life samples. This greatly lowers the requirements of labeled changed buildings, and guarantees the algorithm’s robustness to registration errors caused by parallaxes. To evaluate the proposed method, we chose a wide range of urban areas from an open-source dataset as training and testing areas, and both pixel-based and object-based model evaluation measures were used. Experiments demonstrated our approach was vastly superior: without using any real change samples, it reached 63% average precision (AP) at the object (building instance) level. In contrast, with adequate training samples, other methods—including the most recent CNN-based and generative adversarial network (GAN)-based ones—have only reached 25% AP in their best cases. [full text] [link]
-
, Chi Liu, Mingwei Sun, Yangjun Ou. (2019) Pan-Sharpening Using an Efficient Bidirectional Pyramid Network. In: IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Vol.99:1-15.
Abstract: Pan-sharpening is an important preprocessing step for remote sensing image processing tasks; it fuses a low-resolution multispectral image and a high-resolution (HR) panchromatic (PAN) image to reconstruct a HR multispectral (MS) image. This paper introduces a new end-to-end bidirectional pyramid network for pan-sharpening. The overall structure of the proposed network is a bidirectional pyramid, which permits the network to process MS and PAN images in two separate branches level by level. At each level of the network, spatial details extracted from the PAN image are injected into the upsampled MS image to reconstruct the pan-sharpened image from coarse resolution to fine resolution. Subpixel convolutional layers and the enhanced residual blocks are used to make the network efficient. Comparison of the results obtained with our proposed method and the results using other widely used state-of-the-art approaches confirms that our proposed method outperforms the others in visual appearance and objective indexes. [full text] [link]
-
, Fei Wen, Zhi Gao, Xiao Ling. (2019) A Coarse-to-Fine Framework for Cloud Removal in Remote Sensing Image Sequence. In: IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Vol.99:1-12.

Abstract: Clouds and accompanying shadows, which exist in optical remote sensing images with high possibility, can degrade or even completely occlude certain ground-cover information in images, limiting their applicabilities for Earth observation, change detection, or land-cover classification. In this paper, we aim to deal with cloud contamination problems with the objective of generating cloud-removed remote sensing images. Inspired by low-rank representation together with sparsity constraints, we propose a coarse-to-fine framework for cloud removal in the remote sensing image sequence. Leveraging on group-sparsity constraint, we first decompose the observed cloud image sequence of the same area into the low-rank component, group-sparse outliers, and sparse noise, corresponding to cloud-free land-covers, clouds (and accompanying shadows), and noise respectively. Subsequently, a discriminative robust principal component analysis (RPCA) algorithm is utilized to assign aggressive penalizing weights to the initially detected cloud pixels to facilitate cloud removal and scene restoration. Moreover, we incorporate geometrical transformation into a low-rank model to address the misalignment of the image sequence. Significantly superior to conventional cloud-removal methods, neither cloud-free reference image(s) nor additional operations of cloud and shadow detection are required in our method. Extensive experiments on both simulated data and real data demonstrate that our method works effectively, outperforming many state-of-the-art approaches. [full text] [link]
-
Xunwei Xie, , Xiao Ling, Xiang Wang. (2019) A novel extended phase correlation algorithm based on Log-Gabor filtering for multimodal remote sensing image registration. In: International Journal of Remote Sensing, Vol.16:1-25.
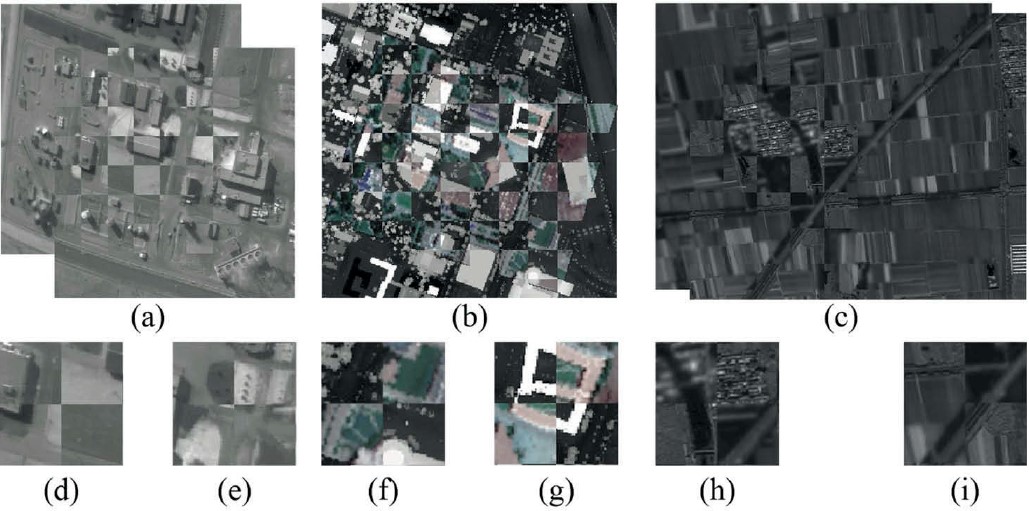

Abstract: Automatic registration of multimodal remote sensing images, which is a critical prerequisite in a range of applications (e.g. image fusion, image mosaic, and image analysis), continues to be a fundamental and challenging problem. In this paper, we propose a novel extended phase correlation algorithm based on Log-Gabor filtering (LGEPC) for the registration of images with nonlinear radiometric differences and geometric differences (e.g. rotation, scale, and translation). Our algorithm focuses on two problems that the traditional extended phase correlation algorithms cannot well handle: 1) significant nonlinear radiometric differences and 2) large-scale differences between image pairs. After an over-complete multi-scale atlas space of the original image is built based on the filtered magnitudes obtained by using Log-Gabor filters with different central frequencies, the phase correlation of the single scale images is extended by LGEPC to atlases phase correlation, which is conducive to solving the problem of large scale and rotation differences between the image pairs. Subsequently, LGEPC eliminates the interface of the significant nonlinear radiometric differences by superimposing multi-scale geometric structural spectra and carrying out the phase correlation module, so that the translation can be well determined. Our experiments on synthetic images demonstrated the rationality and effectiveness of LGEPC, and the experiments on a variety of multimodal images confirmed that LGEPC can ideally achieve pixel-wise registration accuracy for multimodal image pairs that conform to the similarity transformation model. [full text] [link]
-
Xunwei Xie, , Xiang Wang, Daifeng Peng. (2019) A Mixture Likelihood Model of the Anisotropic Gaussian and Uniform Distributions for Accurate Oblique Image Point Matching. In: IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters.

Abstract: In this letter, we propose a mixture likelihood model for accurate oblique image point matching. The basic prior assumption is that the noises are anisotropic with zero mean and different covariances in x- and y-directions for inliers, while the outliers have uniform distribution, which is more suitable for tilted scenes or viewpoint changes. Furthermore, the oblique image point matching problem is formulated as an improved maximum a posteriori (IMAP) estimation of a Bayesian model. In this model, based on the vector field interpolation framework, we combined the mixture likelihood model and our previous adaptive image mismatch removal method, where a two-order term of the regularization coefficient is introduced into the regularized risk function, and a parameter self-adaptive Gaussian kernel function is imposed to construct the regularization term. Subsequently, the expectation-maximization algorithm is utilized to solve the IMAP estimation, in which all the latent variances are able to obtain excellent estimation. Experimental results on real data sets verified that our method was superior to some similar methods in terms of precision and also had better self-adaptability characteristic than some hypothesis-and-verify methods. More experiments on viewpoint changes demonstrated our method's effectiveness without loss of precision-recall tradeoffs, besides significant efficiency improvement. [full text] [link]
-
Mi Wang, , Yanfei Zhong, Xin Huang, Xiangyun Hu, Nengcheng Chen, Bisheng Yang, Jingbin Liu, Huanfeng Shen, Zeming Wang, Liqiong Chen, Jinglin He, Steve McClure. (2018) The State Key Laboratory of Information Engineering in Surveying, Mapping and Remote Sensing. Part of Celebrating 125 Years of Academic Excellence: Wuhan University (1893–2018). In: Science, pp.32-36, Online Publication, 2018.11.28.
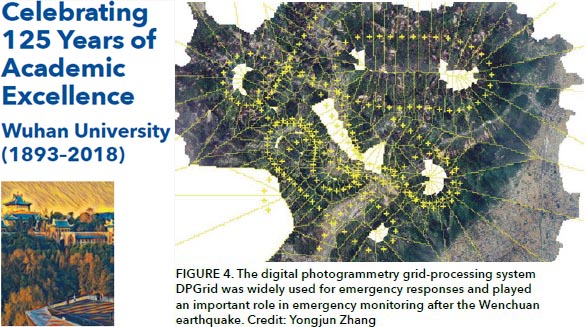
Zhang Zuxun and his team first proposed and investigated the concept of a “full digital automation mapping system,” creating VirtuoZo, an intellectual property of China. The team also advanced a novel digital photogrammetrc grid processing system (DPGrid), which was China’s first set of technologies for fully automatic processing of remotely sensed aerospace images with completely independent intellectual property rights (Figure 4). DPGrid made a crucial breakthrough by transitioning from human–machine interaction to automatic processing, which improves production efficiency by at least 10-fold. Major national engineering projects, such as geographical conditions monitoring and emergency response systems, have applied these innovations widely (Figure 5). The Environmental Systems Research Institute’s ArcGIS system has integrated the core technology of DPGrid, boosting its popularity and use around the world. [full text] [link]
-
Yansheng Li, , Xin Huang, Alan L.Yuille. (2018) Deep Networks under Scene-level Supervision for Multi-class Geospatial Object Detection from Remote Sensing Images. In: ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing Vol.146:182-196.
Abstract: Due to its many applications, multi-class geospatial object detection has attracted increasing research interest in recent years. In the literature, existing methods highly depend on costly bounding box annotations. Based on the observation that scene-level tags provide important cues for the presence of objects, this paper proposes a weakly supervised deep learning (WSDL) method for multi-class geospatial object detection using scene-level tags only. Compared to existing WSDL methods which take scenes as isolated ones and ignore the mutual cues between scene pairs when optimizing deep networks, this paper exploits both the separate scene category information and mutual cues between scene pairs to sufficiently train deep networks for pursuing the superior object detection performance. In the first stage of our training method, we leverage pair-wise scene-level similarity to learn discriminative convolutional weights by exploiting the mutual information between scene pairs. The second stage utilizes point-wise scene-level tags to learn class-specific activation weights. While considering that the testing remote sensing image generally covers a large region and may contain a large number of objects from multiple categories with large size variations, a multi-scale scene-sliding-voting strategy is developed to calculate the class-specific activation maps (CAM) based on the aforementioned weights. Finally, objects can be detected by segmenting the CAM. The deep networks are trained on a seemingly unrelated remote sensing image scene classification dataset. Additionally, the testing phase is conducted on a publicly open multi-class geospatial object detection dataset. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed deep networks dramatically outperform the state-of-the-art methods. [full text] [link]
-
, Xunwei Xie, Xiang Wang, Yansheng Li, Xiao Ling. (2018) Adaptive Image Mismatch Removal With Vector Field Interpolation Based on Improved Regularization and Gaussian Kernel Function. In: IEEE Access Vol.6: 55599-55613.
Abstract: When the regularized kernel methods are utilized in the mismatch removal problem, the regularization coefficient and the choice of kernel function will seriously affect the performance of the methods. In this paper, we propose a method that combines an improved regularization and an adaptive Gaussian kernel function to interpolate the vector fields so as to overcome the issue. We formulated the problem as a modified maximum a posterior estimation of a Bayesian model. In this model, a two-order term of the regularization coefficient is introduced into the regularized risk function in order that the coefficient can be adaptively estimated in the expectation–maximization algorithm. In addition, an adaptive Gaussian kernel function also is imposed to construct the regularization, in which the width of the kernel function is adaptively determined by the diagonal length of the maximum enveloping rectangle of the sample set. Our experimental results verified that our method was robust to large outlier percentages and was slightly superior to some state-of-the-art methods in precision-recall tradeoff and efficiency. The evidence that the performance of our method was insensitive to the remaining inner parameters verified its good self-adaptability. Finally, airborne image pairs were used to demonstrate that our method can establish the feature correspondences even under a discontinuous vector field scene. In addition, we found that our method can obtain higher precision given a residual threshold for special applications such as robust epipolar geometry estimation in computer vision and photogrammetry. [full text] [link]
-
Xianzhang Zhu, Hui Cao, , Kai Tan, Xiao Ling. (2018) Fine Registration for VHR Images Based on Superpixel Registration-Noise Estimation In: IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters 15(10):1615-1620.
Abstract: Local nonlinear geometric distortion is problematic in the registration of very high-resolution (VHR) images. In the standard registration approach, the precision of control points generated from salient feature matching cannot be guaranteed. This letter introduces a novel superpixel registration-noise (RN) estimation method based on a two-step fine registration technique that can be estimate and mitigate the local residual misalignments in VHR images. The first step employs superpixel sparse representation and multiple displacement analysis to estimate RN information of the preregistered image. The second step optimizes the control points obtained in preregistration by combining the RN information and gross error information, and finally fine registers the input image by employing local rectification. The experiments using two data sets generated from Chinese GF2, GF1, and ZY3 satellites are discussed in this letter, and the promising results verify the effectiveness of the proposed new method. [full text] [link]
-
Yansheng Li, , Xin Huang, Jiayi Ma. (2018) Learning Source-Invariant Deep Hashing Convolutional Neural Networks for Cross-Source Remote Sensing Image Retrieval. In: IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing PP(99):1-16.
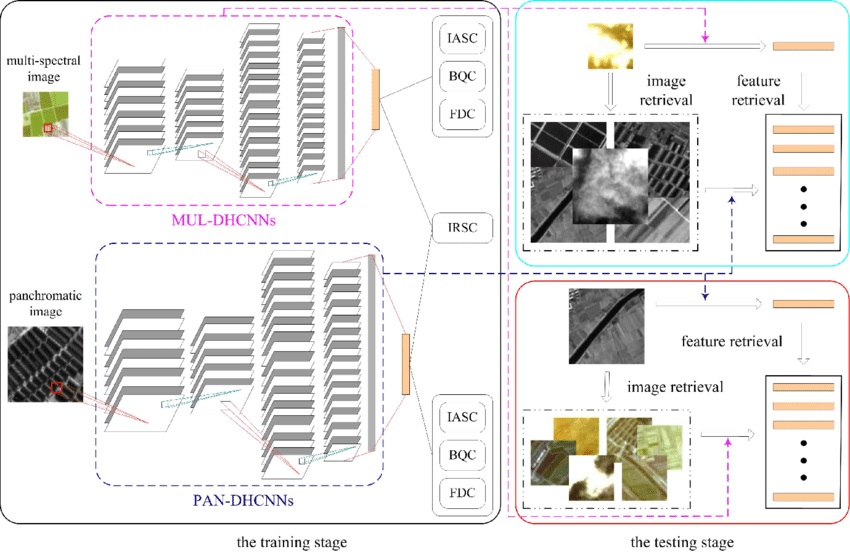
Abstract: Due to the urgent demand for remote sensing big data analysis, large-scale remote sensing image retrieval (LSRSIR) attracts increasing attention from researchers. Generally, LSRSIR can be divided into two categories as follows: uni-source LSRSIR (US-LSRSIR) and cross-source LSRSIR (CS-LSRSIR). More specifically, US-LSRSIR means the inquiry remote sensing image and images in the searching data set come from the same remote sensing data source, whereas CS-LSRSIR is designed to retrieve remote sensing images with a similar content to the inquiry remote sensing image that are from a different remote sensing data source. In the literature, US-LSRSIR has been widely exploited, but CS-LSRSIR is rarely discussed. In practical situations, remote sensing images from different kinds of remote sensing data sources are continually increasing, so there is a great motivation to exploit CS-LSRSIR. Therefore, this paper focuses on CS-LSRSIR. To cope with CS-LSRSIR, this paper proposes source-invariant deep hashing convolutional neural networks (SIDHCNNs), which can be optimized in an end-to-end manner using a series of well-designed optimization constraints. To quantitatively evaluate the proposed SIDHCNNs, we construct a dual-source remote sensing image data set that contains eight typical land-cover categories and $10,000$ dual samples in each category. Extensive experiments show that the proposed SIDHCNNs can yield substantial improvements over several baselines involving the most recent techniques. [full text] [link]
-
Fei Wen, , Zhi Gao, Xiao Ling. (2018) Two-Pass Robust Component Analysis for Cloud Removal in Satellite Image Sequence. In: IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters PP(99):1-5.
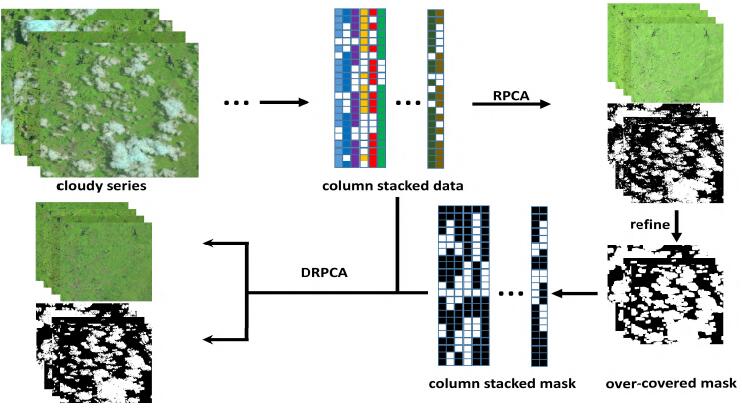
Abstract: Due to the inevitable existence of clouds and their shadows in optical remote sensing images, certain ground-cover information is degraded or even appears to be missing, which limits analysis and utilization. Thus, cloud removal is of great importance to facilitate downstream applications. Motivated by the sparse representation techniques which have obtained a stunning performance in a variety of applications, including target detection, anomaly detection, and so on; we propose a two-pass robust principal component analysis (RPCA) framework for cloud removal in the satellite image sequence. First, a plain RPCA is applied for initial cloud region detection, followed by a straightforward morphological operation to ensure that the cloud region is completely detected. Subsequently, a discriminative RPCA algorithm is proposed to assign aggressive penalizing weights to the detected cloud pixels to facilitate cloud removal and scene restoration. Significantly superior to currently available methods, neither a cloud-free reference image nor a specific algorithm of cloud detection is required in our method. Experiments on both simulated and real images yield visually plausible and numerically verified results, demonstrating the effectiveness of our method. [full text] [link]
-
, Xiang Wang, Xunwei Xie, Yansheng Li. (2018) Salient Object Detection via Recursive Sparse Representation. In: Remote Sensing 10(4):652.
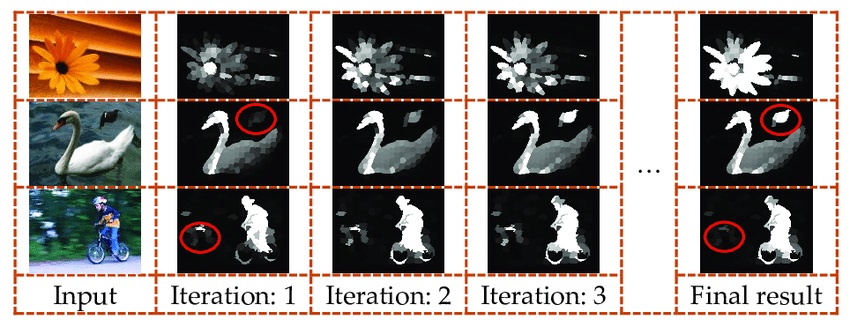
Abstract: Object-level saliency detection is an attractive research field which is useful for many content-based computer vision and remote-sensing tasks. This paper introduces an efficient unsupervised approach to salient object detection from the perspective of recursive sparse representation. The reconstruction error determined by foreground and background dictionaries other than common local and global contrasts is used as the saliency indication, by which the shortcomings of the object integrity can be effectively improved. The proposed method consists of the following four steps: (1) regional feature extraction; (2) background and foreground dictionaries extraction according to the initial saliency map and image boundary constraints; (3) sparse representation and saliency measurement; and (4) recursive processing with a current saliency map updating the initial saliency map in step 2 and repeating step 3. This paper also presents the experimental results of the proposed method compared with seven state-of-the-art saliency detection methods using three benchmark datasets, as well as some satellite and unmanned aerial vehicle remote-sensing images, which confirmed that the proposed method was more effective than current methods and could achieve more favorable performance in the detection of multiple objects as well as maintaining the integrity of the object area. [full text] [link]
-
Yansheng Li, . (2017) Robust Infrared Small Target Detection Using Local Steering Kernel Reconstruction. In: Pattern Recognition 77.
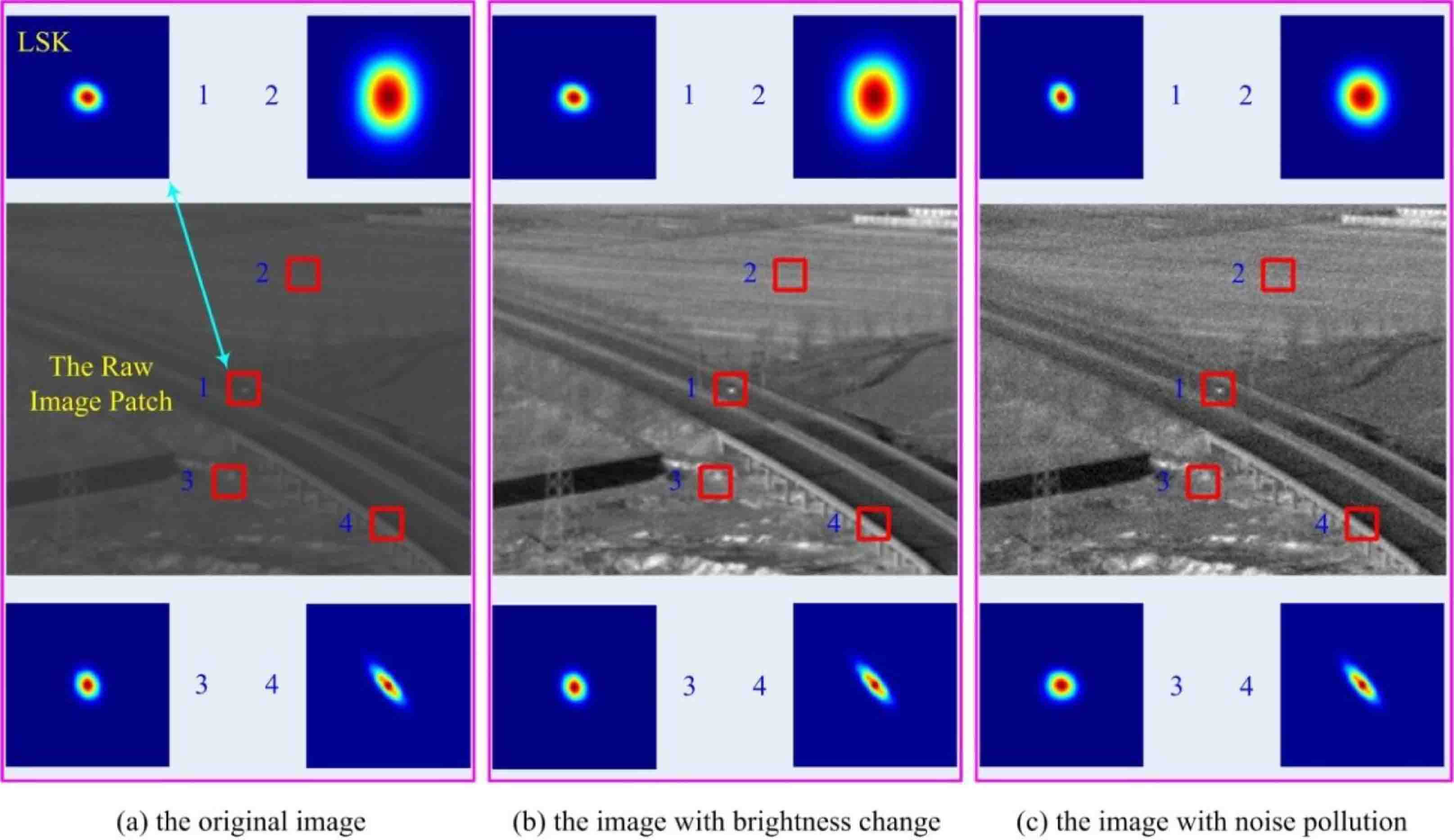
Abstract: Because infrared small target detection plays a crucial role in infrared monitoring and early warning systems, it has been the subject of considerable research. Although many infrared small target detection approaches have been proposed, how to robustly detect small targets in poor quality infrared images remains a challenge. Since existing feature descriptors are often sensitive to the quality of infrared images, this paper advocates the use of a local steering kernel (LSK) to encode the infrared image patch because the LSK method can provide robust estimation of local intrinsic structure, even for poor quality images. Furthermore, this paper proposes a novel local adaptive contrast measure based on LSK reconstruction (LACM-LSK) for infrared small target detection. To demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach, a diverse test dataset, including six infrared image sequences with different backgrounds, was collected. Extensive experiments on the test dataset confirm that the proposed infrared small target detection approach can achieve better detection performance than state-of-the-art approaches. [full text] [link]
-
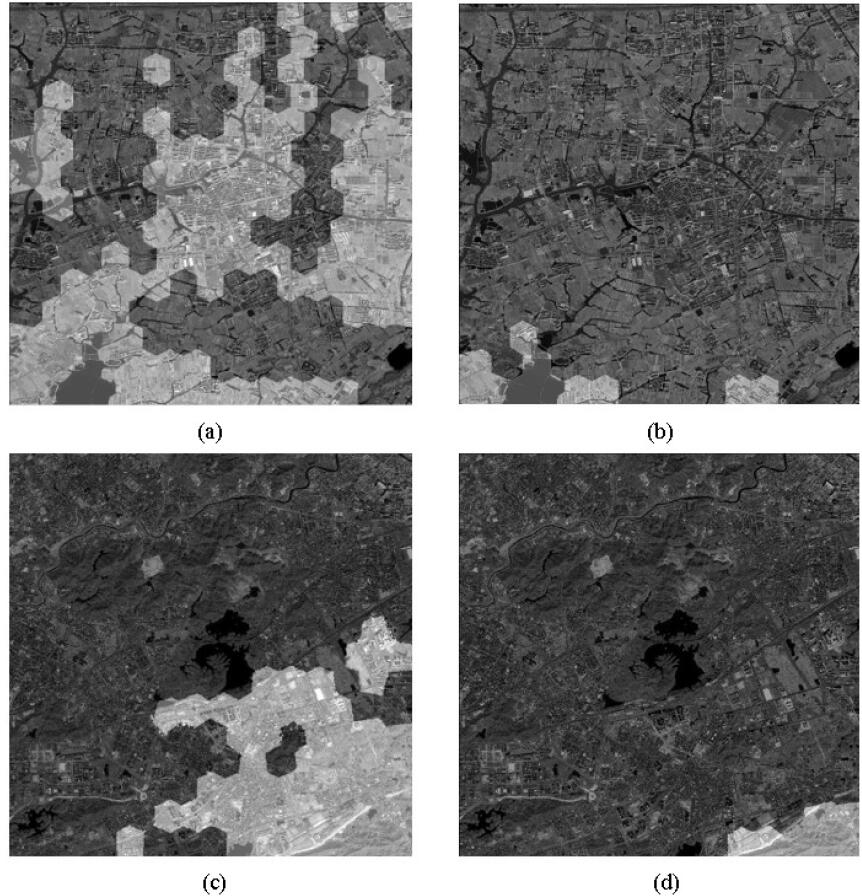
, Daifeng Peng, Xu Huang. (2017) Object-Based Change Detection for VHR Images Based on Multiscale Uncertainty Analysis. In: IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters PP(99):1-5.
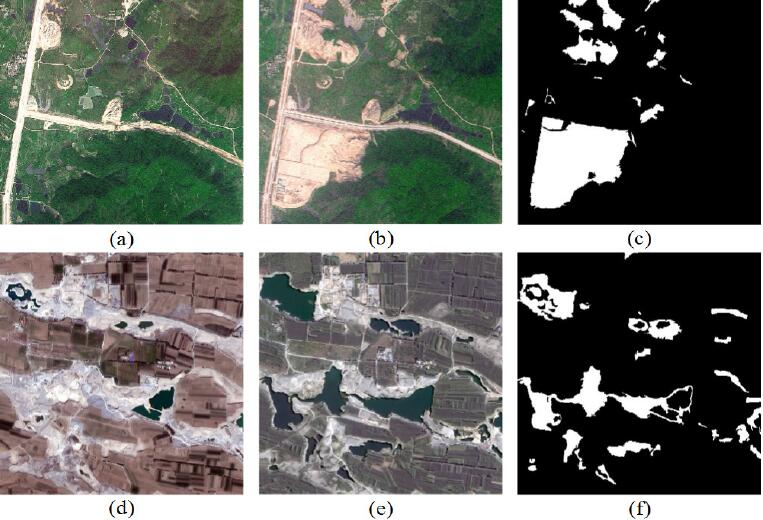
Abstract: Scale is of great significance in image analysis and interpretation. In order to utilize scale information, multiscale fusion is usually employed to combine change detection (CD) results from different scales. However, CD results from different scales are usually treated independently, which ignores the scale contextual information. To overcome this drawback, this letter introduces a novel object-based change detection (OBCD) technique for unsupervised CD in very high-resolution (VHR) images by incorporating multiscale uncertainty analysis. First, two temporal images are stacked and segmented using a series of optimal segmentation scales ranging from coarse to fine. Second, an initial CD result is obtained by fusing the pixel-based CD result and OBCD result based on Dempter-Shafer (DS) evidence theory. Third, multiscale uncertainty analysis is implemented from coarse scale to fine scale by support vector machine classification. Finally, a CD map is generated by combining all the available information in all the scales. The experimental results employing SPOT5 and GF-1 images demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed approach. [full text] [link]
-
Yansheng Li, , Xin Huang, Hu Zhu, Jiayi Ma. (2017) Large-Scale Remote Sensing Image Retrieval by Deep Hashing Neural Networks. In: IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing PP(99).

Abstract: As one of the most challenging tasks of remote sensing big data mining, large-scale remote sensing image retrieval has attracted increasing attention from researchers. Existing large-scale remote sensing image retrieval approaches are generally implemented by using hashing learning methods, which take handcrafted features as inputs and map the high-dimensional feature vector to the low-dimensional binary feature vector to reduce feature-searching complexity levels. As a means of applying the merits of deep learning, this paper proposes a novel large-scale remote sensing image retrieval approach based on deep hashing neural networks (DHNNs). More specifically, DHNNs are composed of deep feature learning neural networks and hashing learning neural networks and can be optimized in an end-to-end manner. Rather than requiring to dedicate expertise and effort to the design of feature descriptors, we can automatically learn good feature extraction operations and feature hashing mapping under the supervision of labeled samples. To broaden the application field, DHNNs are evaluated under two representative remote sensing cases: scarce and sufficient labeled samples. To make up for a lack of labeled samples, DHNNs can be trained via transfer learning for the former case. For the latter case, DHNNs can be trained via supervised learning from scratch with the aid of a vast number of labeled samples. Extensive experiments on one public remote sensing image data set with a limited number of labeled samples and on another public data set with plenty of labeled samples show that the proposed remote sensing image retrieval approach based on DHNNs can remarkably outperform state-of-the-art methods under both of the examined conditions. [full text] [link]
-
Yansong Duan, Xiao Ling, , Zuxun Zhang, Xinyi Liu, Kun Hu. (2017) A Simple and Efficient Method for Radial Distortion Estimation by Relative Orientation. In: IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing PP(99):1-9.
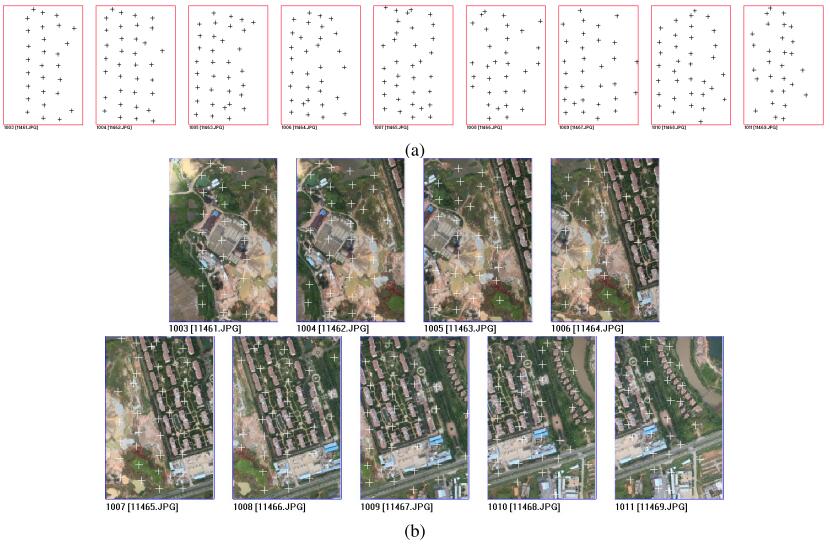
Abstract: In order to solve the accuracy problem caused by lens distortions of nonmetric digital cameras mounted on an unmanned aerial vehicle, the estimation for initial values of lens distortion must be studied. Based on the fact that radial lens distortions are the most significant of lens distortions, a simple and efficient method for radial lens distortion estimation is proposed in this paper. Starting from the coplanar equation, the geometric characteristics of the relative orientation equations are explored. This paper further proves that the radial lens distortion can be linearly estimated in a continuous relative orientation model. The proposed procedure only requires a sufficient number of point correspondences between two or more images obtained by the same camera; thus it is suitable for a natural scene where the lack of straight lines and calibration objects precludes most previous techniques. Both computer simulation and real data have been used to test the proposed method; the experimental results show that the proposed method is easy to use and flexible. [full text] [link]
-
Chang li, Xiaojuan Liu, , Zuxun Zhang. (2017) A Stepwise-then-Orthogonal Regression (STOR) with quality control for Optimizing the RFM of High-Resolution Satellite Imagery. In: Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing 83(9):611-620.
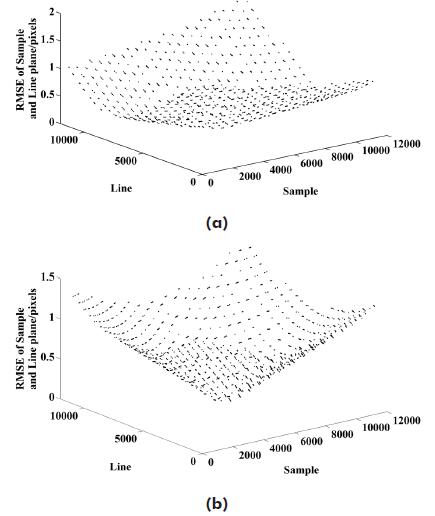
Abstract: There are two major problems in Rational Function Model (RFM) solution: (a) Data source error, including gross error, random error, and systematic error; and (b) Model error, including over-parameterization and over-correction issues caused by unnecessary RFM parameters and exaggeration of random error in constant term of error-in-variables (EIV) model, respectively. In order to solve two major problems simultaneously, we propose a new approach named stepwise-thenorthogonal regression (STOR) with quality control. First, RFM parameters are selected by stepwise regression with gross error detection. Second, the revised orthogonal distance regression is utilized to adjust random error and address the overcorrection problem. Third, systematic error is compensated by Fourier series. The performance of conventional strategies and the proposed STOR are evaluated by control and check grids generated from SPOT5 high-resolution imagery. Compared with the least squares regression, partial least squares regression, ridge regression, and stepwise regression, the proposed STOR shows a significant improvement in accuracy. [full text] [link]
-
Yanfeng Zhang, , Yunjun ZhangYunjun Zhang, Zongze Zhao. (2017) A Two-Step Semiglobal Filtering Approach to Extract DTM From Middle Resolution DSM. In: IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters PP(99):1-5.
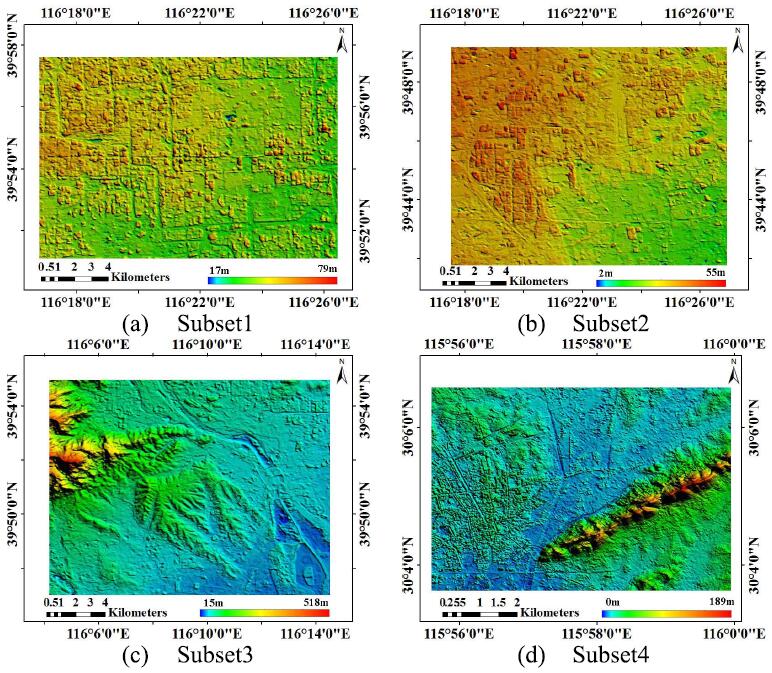
Abstract: Many filtering algorithms have been developed to extract the digital terrain model (DTM) from dense urban light detection and ranging data or the high-resolution digital surface model (DSM), assuming a smooth variation of topographic relief. However, this assumption breaks for a middle-resolution DSM because of the diminished distinction between steep terrains and nonground points. This letter introduces a two-step semiglobal filtering (TSGF) workflow to separate those two components. The first SGF step uses the digital elevation model of the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission to obtain a flat-terrain mask for the input DSM; then, a segmentation-constrained SGF is used to remove the nonground points within the flat-terrain mask while maintaining the shape of the terrain. Experiments are conducted using DSMs generated from Chinese ZY3 satellite imageries, verified the effectiveness of the proposed method. Compared with the conventional progressive morphological filter method, the usage of flat-terrain mask reduced the average root-mean-square error of DTM from 9.76 to 4.03 m, which is further reduced to 2.42 m by the proposed TSGF method. [full text] [link]
-
Yi Wan, . (2017) The P2L method of mismatch detection for push broom high-resolution satellite images. In: ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing 130:317-328.
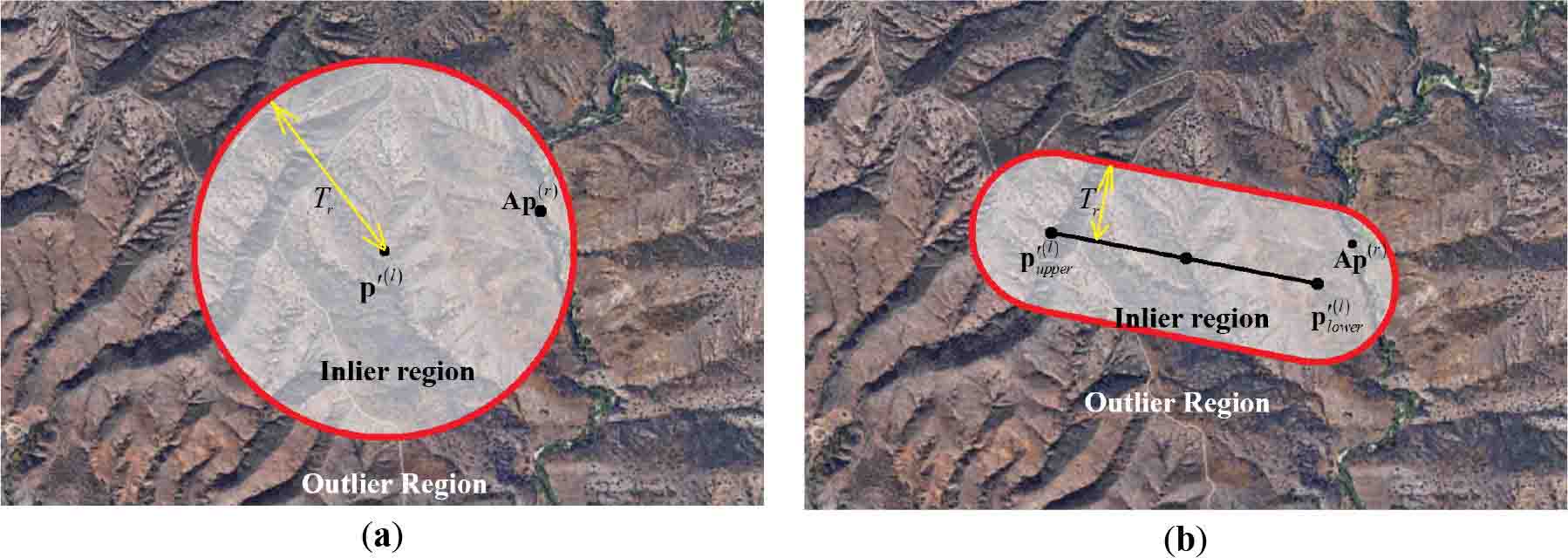

Abstract: RANSAC-based mismatch detection methods are widely used in the geometric registration of images. Despite their prevalence, setting the detection thresholds for different situations continues to be difficult without an appropriate geometric model. In high-resolution satellite images, simple image-space transformations are commonly influenced by the terrain or elevation errors. This paper introduces a new method, called the P2L method, which uses the distance between the transformed right image point and the segment of the corresponding epipolar line to distinguish the correct matches and mismatches. The affine model of the P2L method is solved to transform the right image points towards the segment of the epipolar line. The images for demonstration were acquired by GeoEye-1, Ikonos-2, and Ziyuan-3; and each type of image pairs had different intersection angles to explore the influence of the elevation error. The correct matches were manually collected and the mismatches were simulated. The experiments in this paper, which used only correct matches, demonstrated that this method was very robust with one specific threshold (five pixels) and was suitable for all the image pairs. The experiments using simulated mismatches and real matching points demonstrated that this method was able to distinguish most of the mismatches; and even for the image pair that had a 54-degree intersection angle, the ratio of mismatches was reduced from 81% to 11%. [full text] [link]
-
Daifeng Peng, . (2017) Object-based change detection from satellite imagery by segmentation optimization and multi-features fusion. In: International Journal of Remote Sensing 38(13):3886-3905.
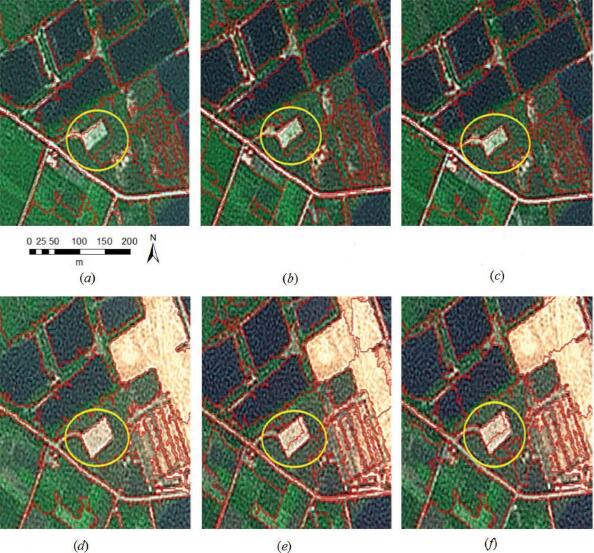

Abstract: This article presents a novel object-based change detection (OBCD) approach in high-resolution remote-sensing images by means of combining segmentation optimization and multi-features fusion. In the segmentation optimization, objects with optimized boundaries and proper sizes are generated by object intersection and merging (OIM) processes, which ensures the accurate information extraction from image objects. Within multi-features fusion and change analysis, the Dempster and Shafer (D-S) evidence theory and the Expectation-Maximization (EM) algorithm are implemented, which effectively utilize multidimensional features besides avoiding the selection of an appropriate change threshold. The main advantages of our proposed method lie in the improvement of object boundary and the fuzzy fusion of multi-features information. The proposed approach is evaluated using two different high-resolution remote-sensing data sets, and the qualitative and quantitative analyses of the results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach. [full text] [link]
-
Rujun Cao, , Xinyi Liu, Zongze Zhao. (2017) Roof plane extraction from airborne lidar point clouds. In: International Journal of Remote Sensing 38(12):3684-3703.
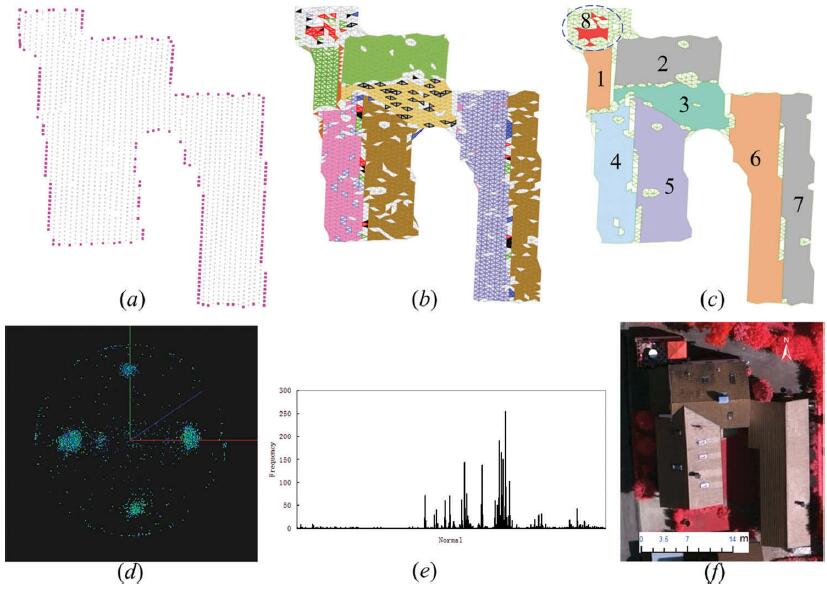
Abstract: Planar patches are important primitives for polyhedral building models. One of the key challenges for successful reconstruction of three-dimensional (3D) building models from airborne lidar point clouds is achieving high quality recognition and segmentation of the roof planar points. Unfortunately, the current automatic extraction processes for planar surfaces continue to suffer from limitations such as sensitivity to the selection of seed points and the lack of computational efficiency. In order to address these drawbacks, a new fully automatic segmentation method is proposed in this article, which is capable of the following: (1) processing a roof point dataset with an arbitrary shape; (2) robustly selecting the seed points in a parameter space with reduced dimensions; and (3) segmenting the planar patches in a sub-dataset with similar attributes when region growing in the object space. The detection of seed points in the parameter space was improved by mapping the accumulator array to a 1D space. The range for region growing in the object space was reduced by an attribute similarity measure that split the roof dataset into candidate and non-candidate subsets. The experimental results confirmed that the proposed approach can extract planar patches of building roofs robustly and efficiently. [full text] [link]
-
Rujun Cao, , Xinyi Liu, Zongze Zhao. (2017) 3D Building Roof Reconstruction from Airborne LiDAR Point Clouds--a Framework Based on a Spatial Database. In: International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 31(7):1359-1380.
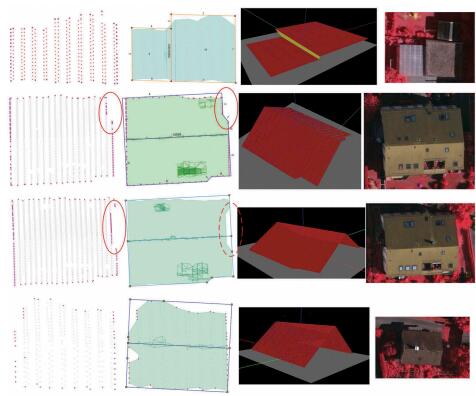
Abstract: Three-dimensional (3D) building models are essential for 3D Geographic Information Systems and play an important role in various urban management applications. Although several light detection and ranging (LiDAR) data-based reconstruction approaches have made significant advances toward the fully automatic generation of 3D building models, the process is still tedious and time-consuming, especially for massive point clouds. This paper introduces a new framework that utilizes a spatial database to achieve high performance via parallel computation for fully automatic 3D building roof reconstruction from airborne LiDAR data. The framework integrates data-driven and model-driven methods to produce building roof models of the primary structure with detailed features. The framework is composed of five major components: (1) a density-based clustering algorithm to segment individual buildings, (2) an improved boundary-tracing algorithm, (3) a hybrid method for segmenting planar patches that selects seed points in parameter space and grows the regions in spatial space, (4) a boundary regularization approach that considers outliers and (5) a method for reconstructing the topological and geometrical information of building roofs using the intersections of planar patches. The entire process is based on a spatial database, which has the following advantages: (a) managing and querying data efficiently, especially for millions of LiDAR points, (b) utilizing the spatial analysis functions provided by the system, reducing tedious and time-consuming computation, and (c) using parallel computing while reconstructing 3D building roof models, improving performance. [full text] [link]
-
Lei Yu, , Mingwei Sun, Yihui Lu. (2017) Automatic Reference Image Selection for Color Balancing in Remote Sensing Imagery Mosaic. In: IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters PP(99):1-5.
Abstract: Selection of a reference image is an important step in color balancing. However, the past research and currently available methods do not focus on it, leading to the lack of an effective way to select the reference image for color balancing in remote sensing imagery mosaic. This letter proposes a novel automatic reference image selection method that aims to select the reference images by assessing multifactors according to the land surface types of the target images. The proposed method addresses the limitations caused by the use of a single assessment factor as well as the selection of a single image as the reference in traditional methods. In addition, the proposed method has a wider range of applications than those requiring no reference image. The visual experimental results indicate that the proposed method can select the suitable reference images, which benefits the color balancing result, and outperforms the other comparative methods.Moreover, the absolute mean value of skewness metric of the proposed method is 0.0831, which is lower than the values of the other comparison methods. It indicates that the result of the proposed method had the best performance in the color information. The quantitative analyses with the metric of absolute difference of mean value indicate that the proposed method has a good ability in maintaining the spectral information, and the spectral changing rates had been reduced at least 10.66% by the proposed method when compared with the other methods. [full text] [link]
-
, Lei Yu, Mingwei Sun, Xinyu Zhu. (2017) A Mixed Radiometric Normalization Method for Mosaicking of High-Resolution Satellite Imagery. In: IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Vol.55 No.5: 2972 - 2984.
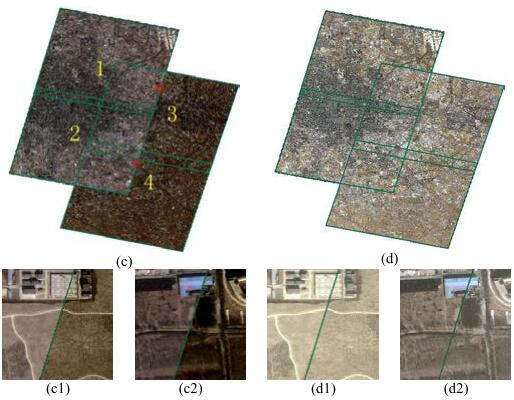

Abstract: A new mixed radiometric normalization (MRN) method is introduced in this paper which aims to eliminate the radiometric difference in image mosaicking. The radiometric normalization methods can be classified as the absolute and relative approaches in traditional solutions. Though the absolute methods could get the precise surface reflectance values of the images, rigorous conditions required for them are usually difficult to obtain, which makes the absolute methods impractical in many cases. The relative methods, which are simple and practicable, are more widely applied. However, the standard for designating the reference image needed for these methods is not unified. Moreover, the color error propagation and the two-body problems are common obstacles for the relative methods. The proposed MRN approach combines absolute and relative radiometric normalization methods, by which the advantages of both can be fully used and the limitations can be effectively avoided. First, suitable image after absolute radiometric calibration is selected as the reference image. Then, the invariant feature probability between the pixels of the target image and that of the reference image is obtained. Afterward, an adaptive local approach is adopted to obtain a suitable linear regression model for each block. Finally, a bilinear interpolation method is employed to obtain the radiometric calibration parameters for each pixel. Moreover, the CIELAB color space is adopted to evaluate the results quantitatively. Experimental results of ZY-3, GF-1, and GF-2 data indicate that the proposed method can eliminate the radiometric differences between images from the same or even different sensors. [full text] [link]
-
Yanfeng Zhang, , Delin Mo, Yi Zhang, Xin Li. (2017) Direct Digital Surface Model Generation by Semi-Global Vertical Line Locus Matching. In: Remote Sensing , 214-233.

Abstract: As the core issue for Digital Surface Model (DSM) generation, image matching is often implemented in photo space to get disparity or depth map. However, DSM is generated in object space with additional processes such as reference image selection, disparity maps fusion or depth maps merging, and interpolation. This difference between photo space and object space leads to process complexity and computation redundancy. We propose a direct DSM generation approach called the semi-global vertical line locus matching (SGVLL), to generate DSM with dense matching in the object space directly. First, we designed a cost function, robust to the pre-set elevation step and projection distortion, and detected occlusion during cost calculation to achieve a sound photo-consistency measurement. Then, we proposed an improved semi-global cost aggregation with guidance of true-orthophoto to obtain superior results at weak texture regions and slanted planes. The proposed method achieves performance very close to the state-of-the-art with less time consumption, which was experimentally evaluated and verified using nadir aerial images and reference data. [full text] [link]
-
Daifeng Peng, . (2017) Object-based change detection method using refined Markov random field. In: Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, Vol.11 No.1: 016024-1-11.
Abstract: In order to fully consider the local spatial constraints between neighboring objects in object-based change detection (OBCD), an OBCD approach is presented by introducing a refined Markov random field (MRF). First, two periods of images are stacked and segmented to produce image objects. Second, object spectral and textual histogram features are extracted and G-statistic is implemented to measure the distance among different histogram distributions. Meanwhile, object heterogeneity is calculated by combining spectral and textual histogram distance using adaptive weight. Third, an expectation-maximization algorithm is applied for determining the change category of each object and the initial change map is then generated. Finally, a refined change map is produced by employing the proposed refined object-based MRF method. Three experiments were conducted and compared with some state-of-the-art unsupervised OBCD methods to evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed method. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method obtains the highest accuracy among the methods used in this paper, which confirms its validness and effectiveness in OBCD. [full text] [link]
-
Dongliang Wang, Wei Cao, Xiaoping Xin, Quanqin Shao, Matthew Brolly, Jianhua Xiao, . (2017) Using Vector Building Maps to Aid in Generating Seams for Low-Attitude Aerial Orthoimage Mosaicking. In: Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, Vol.125: 207-224.

Abstract: A novel seam detection approach based on vector building maps is presented for low-attitude aerial orthoimage mosaicking. The approach tracks the centerlines between vector buildings to generate the candidate seams that avoid crossing buildings existing in maps. The candidate seams are then refined by considering their surrounding pixels to minimize the visual transition between the images to be mosaicked. After the refinement of the candidate seams, the final seams further bypass most of the buildings that are not updated into vector maps. Finally, three groups of aerial imagery from different urban densities are employed to test the proposed approach. The experimental results illustrate the advantages of the proposed approach in avoiding the crossing of buildings. The computational efficiency of the proposed approach is also significantly higher than that of Dijkstra’s algorithm. [full text] [link]
-
Lei Yu, . (2016) Colour Balancing of Satellite Imagery Based on Colour Reference Library. In :International Journal of Remote Sensing, Vol.37 N.o2: 5763–5785.
Abstract: Generating mosaics of images obtained at different times is a challenging task because of the radiometric differences between the adjacent images introduced by the solar incident angle, atmosphere, and illumination condition. For most of the existing colour-balancing methods, the standard for determining the reference image is not unified, thus yielding different calibration results. Besides, traditional methods may suffer from colour error propagation and the two-body problems. A novel colour-balancing method for satellite imagery based on a colour reference library is proposed in this article, which aims to eliminate the effect of colour difference between different images for visually appealing and seamless image mosaicking. The proposed method contains two parts: the establishment of a colour reference library and the colour-balancing method based on it. Colour reference library is a database storing colour and other related information from the existing mosaic imagery. The colour information of the existing mosaic imagery is visually appealing and consistent with human visual perception. By automatically selecting appropriate colour reference information from the colour reference library according to the geographical scope and acquisition season information of the target images, the proposed approach provides effective solutions for choosing suitable reference image, colour error propagation, and the two-body problem in traditional colour-balancing methods. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed approach performs well in the colour-balancing process. [full text] [link]
-
Kai Tan, , Xin Tong. (2016) Cloud Extraction from Chinese High Resolution Satellite Imagery by Probabilistic Latent Semantic Analysis and Object-Based Machine Learning. In: Remote Sensing, Vol.8 No11 :963.
Abstract: Automatic cloud extraction from satellite imagery is a vital process for many applications in optical remote sensing since clouds can locally obscure the surface features and alter the reflectance. Clouds can be easily distinguished by the human eyes in satellite imagery via remarkable regional characteristics, but finding a way to automatically detect various kinds of clouds by computer programs to speed up the processing efficiency remains a challenge. This paper introduces a new cloud detection method based on probabilistic latent semantic analysis (PLSA) and object-based machine learning. The method begins by segmenting satellite images into superpixels by Simple Linear Iterative Clustering (SLIC) algorithm while also extracting the spectral, texture, frequency and line segment features. Then, the implicit information in each superpixel is extracted from the feature histogram through the PLSA model by which the descriptor of each superpixel can be computed to form a feature vector for classification. Thereafter, the cloud mask is extracted by optimal thresholding and applying the Support Vector Machine (SVM) algorithm at the superpixel level. The GrabCut algorithm is then applied to extract more accurate cloud regions at the pixel level by assuming the cloud mask as the prior knowledge. When compared to different cloud detection methods in the literature, the overall accuracy of the proposed cloud detection method was up to 90 percent for ZY-3 and GF-1 images, which is about a 6.8 percent improvement over the traditional spectral-based methods. The experimental results show that the proposed method can automatically and accurately detect clouds using the multispectral information of the available four bands. [full text] [link]
-
Maoteng Zheng, Junfeng Zhu, Xiaodong Xiong, Shunping Zhou, . (2016) 3D Model Reconstruction with Common Hand-held Cameras. In: Virtual Reality, Vol.20: 2211-235.
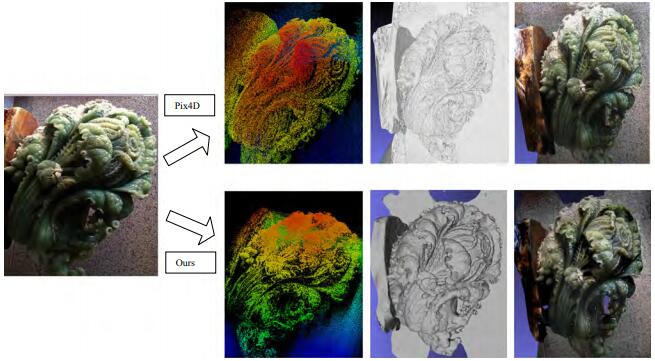
Abstract: A 3D model reconstruction workflow with hand-held cameras is developed. The exterior and interior orientation models combined with the state-of-the-art structure from motion and multi-view stereo techniques are applied to extract dense point cloud and reconstruct 3D model from digital images. An overview of the presented 3D model reconstruction methods is given. The whole procedure including tie point extraction, relative orientation, bundle block adjustment, dense point production and 3D model reconstruction is all reviewed in brief. Among them, we focus on bundle block adjustment procedure; the mathematical and technical details of bundle block adjustment are introduced and discussed. Finally, four scenes of images collected by hand-held cameras are tested in this paper. The preliminary results have shown that sub-pixel (< 1 pixel) accuracy can be achieved with the proposed exterior–interior orientation models and satisfactory 3D models can be reconstructed using images collected by hand-held cameras. This work can be applied in indoor navigation, crime scene reconstruction, heritage reservation and other applications in geosciences. [full text] [link]
-
Xiao Ling, , Jinxin Xiong, Xu Huang, Zhipeng Chen. (2016) An Image Matching Algorithm Integrating Global SRTM and Image Segmentation for Multi-Source Satellit. In: Remote Sensing,672–690.
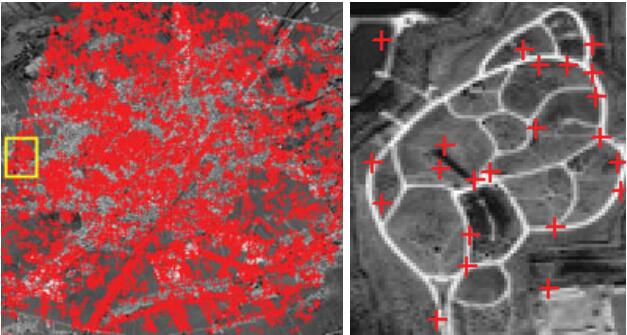
Abstract: This paper presents a novel image matching method for multi-source satellite images, which integrates global Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) data and image segmentation to achieve robust and numerous correspondences. This method first generates the epipolar lines as a geometric constraint assisted by global SRTM data, after which the seed points are selected and matched. To produce more reliable matching results, a region segmentation-based matching propagation is proposed in this paper, whereby the region segmentations are extracted by image segmentation and are considered to be a spatial constraint. Moreover, a similarity measure integrating Distance, Angle and Normalized Cross-Correlation (DANCC), which considers geometric similarity and radiometric similarity, is introduced to find the optimal correspondences. Experiments using typical satellite images acquired from Resources Satellite-3 (ZY-3), Mapping Satellite-1, SPOT-5 and Google Earth demonstrated that the proposed method is able to produce reliable and accurate matching results. [full text] [link]
-
Yansheng Li, , Chao Tao, Hu Zhu. (2016) A Novel Spatio-Temporal Saliency Approach for Robust Dim Moving Target Detection from Airborne Infrared Image Sequences. In: International Journal of Remote Sensing, Vol.369 :548–563.
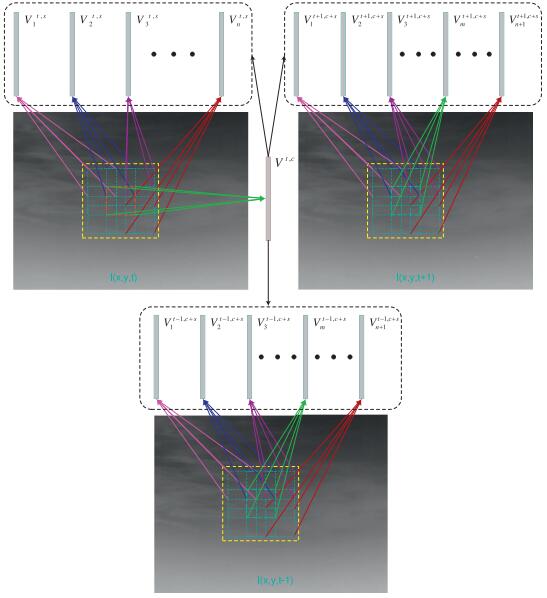
Abstract: Dim moving target detection from infrared image sequences, which lags behind the visual perception ability of humans, has attracted considerable interest from researchers due to its crucial role in airborne surveillance systems. This paper proposes a novel spatio-temporal saliency model to cope with the infrared dim moving target detection problem. Based on a closed-form solution derived from regularized feature reconstruction, a local adaptive contrast operation is proposed, whereby the spatial saliency map and the temporal saliency map can be calculated on the spatial domain and the temporal domain. In order to depict the motion consistency characteristic of the moving target, this paper also proposes a transmission operation to generate the trajectory prediction map. The fused result of the spatial saliency map, the temporal saliency map, and the trajectory prediction map is called the “spatio-temporal saliency map” in this paper, from which the target of interest can be easily segmented. A diverse test dataset comprised of three infrared image sequences under different backgrounds was collected to evaluate the proposed model; and extensive experiments confirmed that the proposed spatio-temporal saliency model can achieve much better detection performance than the state-of-the-art approaches. [full text] [link]
-
Maoteng Zheng, , ShunpingZhou, JunfengZhu, XiaodongXiong. (2016) Bundle block adjustment of large-scale remote sensing data with Block-based Sparse Matrix Compression combined with Preconditioned Conjugate Gradient. In: Computers and Geosciences, Vol.92 : 70-78.
Abstract: In recent years, new platforms and sensors in photogrammetry, remote sensing and computer vision areas have become available, such as Unmanned Aircraft Vehicles (UAV), oblique camera systems, common digital cameras and even mobile phone cameras. Images collected by all these kinds of sensors could be used as remote sensing data sources. These sensors can obtain large-scale remote sensing data which consist of a great number of images. Bundle block adjustment of large-scale data with conventional algorithm is very time and space (memory) consuming due to the super large normal matrix arising from large-scale data. In this paper, an efficient Block-based Sparse Matrix Compression (BSMC) method combined with the Preconditioned Conjugate Gradient (PCG) algorithm is chosen to develop a stable and efficient bundle block adjustment system in order to deal with the large-scale remote sensing data. The main contribution of this work is the BSMC-based PCG algorithm which is more efficient in time and memory than the traditional algorithm without compromising the accuracy. Totally 8 datasets of real data are used to test our proposed method. Preliminary results have shown that the BSMC method can efficiently decrease the time and memory requirement of large-scale data. [full text] [link]
-
Chang Li, . (2016) Automatic Keyline Recognition and 3D Reconstruction for Quasi-planar Facades in Close-range Images. In: The Photogrammetric Record, Vol.31 No.153: 29–50.

Abstract: Critical keylines, such as concave and convex edges of a building façade, can be lost in photogrammetric recognition procedures. To solve this problem and to reconstruct quasi‐planar 3D façades automatically and precisely, a set of algorithms and techniques for the automatic recognition of lines and 3D reconstruction is proposed. This includes: (1) a procedure for line‐segment matching that satisfies the spatial requirements of a 3D scene based on “global independence” and “local dependence”; (2) a technique of generalised point bundle block adjustment combined with spatial line constraints (in the form of virtual observations) to control the propagation of error; and (3) the methods of perceptual organisation, plane fitting and plane–plane intersection are suggested to acquire the critical keylines corresponding to concave and convex building edges. Experimental results show that these new algorithms are feasible and applicable to recognition and 3D reconstruction. Recommendations for recognition methods are provided depending on whether or not a priori topological relationships are available between the planes under consideration. [full text] [link]
-
,Yi Wan. (2016) DEM-assisted RFM Block Adjustment of Pushbroom Nadir Viewing HRS Imagery. In: IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Vol.54 No.2: 1025-1034.
Abstract: Nadir viewing satellite image is an effective data source to generate orthomosaics. Because of the georeferencing error of satellite images, block adjustment is the first step of orthomosaic generation over a large area. However, the geometric relationship of the neighboring orbits of the nadir viewing images is not rigid enough. This paper proposes a new rational function model (RFM) block adjustment approach that constrains the tie point elevation to enhance the relative geometric rigidity. By interpolating the elevations of tie points in a digital elevation model(DEM) and estimating the a priori errors of the interpolated elevations, better overall relative accuracy is obtained, and the local optimal solution problem is avoided. By constraining the adjustedmodel parameters according to the a priori error of RFMs, block adjustment without ground control point (GCP) is performed. By optimal initializing the object–space positions of tie points with multi-backprojection method, the needed iteration times of block adjustment are reduced. The proposed approach is investigated with 46 Ziyuan-3 sensor-corrected images, a 1:50 000 scale DEM, and 586 GCPs. Compared with Teo’s approach that constrains the horizontal coordinates and elevations of tie points, the approach in this paper converges much faster when the GCPs are sparse, and meanwhile, the absolute and relative accuracy of the two approaches are almost the same. The result of block adjustment with only four GCPs shows that no accuracy degeneration occurred in the test area and the root-mean-square error of independent check point reaches about 1.5 ground resolutions. Different DEMs and number of tie points are used to investigate whether the block adjustment result is influenced by these factors. The results show that better DEM accuracy and denser tie points do improve the accuracy when the images have large side-sway angles. The proposed approach is also tested with 5118 IKONOS-2 images that cover the southern Europe without GCP. The result shows that the relative mosaicking accuracy is much better than that of Grodecki’s approach. [full text] [link]
-
Zongze Zhao, Yansong Duan, , Rujun Cao. (2016) Extracting Buildings from and Regularizing Boundaries in Airborne LiDAR Data Using Connected Operators. In:International Journal of Remote Sensing, Vol.37 No 4 :889-912.
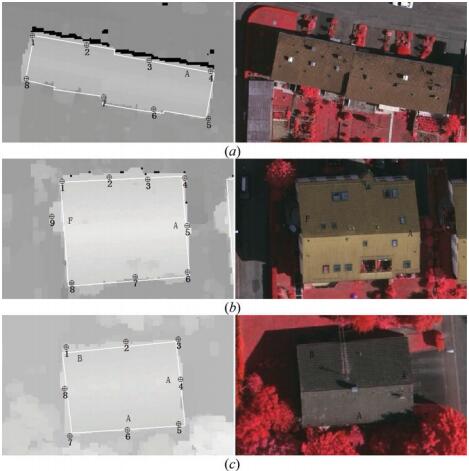
Abstract: The location of building boundary is a crucial prerequisite for geographical condition monitoring, urban management, and building reconstruction. This paper presents a framework that employs a series of algorithms to automatically extract building footprints from airborne (light detection and ranging (lidar)) data and image. Connected operators are utilized to extract building regions from lidar data, which would not produce new contours nor change their position and have very good contour-preservation properties. First, the building candidate regions are separated from lidar-derived digital surface model (DSM) based on a new method proposed within this paper using connected operators, and trees are removed based on the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) value of image. Then, building boundaries are identified and building boundary lines are traced by ‘sleeve’ line simplification method. Finally, the principal directions of buildings are used to regularize the directions of building boundary lines. International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing (ISPRS) data sets in Vaihingen whose point spacing is about 0.4 m from urbanized areas were employed to test the proposed framework, and three test areas were selected. A quantitative analysis showed that the method proposed within this paper was effective and the average offset values of simple and complex building boundaries were 0.2–0.4 m and 0.3–0.6 m, respectively. [full text] [link]
-
Maoteng Zheng,. (2016) DEM-Aided Bundle Adjustment with Multisource Satellite Imagery: ZY-3 and GF-1 in Large Areas. In:IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, Vol.13 No.6: 880–884.
Abstract: In this letter, a new digital elevation model (DEM)-aided bundle block adjustment (BBA) method is proposed which utilizes a rational-polynomial-coefficient affine transformation model and a preconditioned conjugate gradient (PCG) algorithm with multisource satellite imagery (ZY-3 and GF-1) for producing and updating ortho maps of large areas. To deal with the weak geometry of the large blocks, a reference DEM is used in this method as an additional constraint in the BBA. The PCG algorithm is applied to solve the large normal matrix produced by the massive data of the large areas. Our proposed method was tested on three blocks of real data collected by GF-1 panchromatic and multispectral sensors and ZY-3 three-line-camera sensors. The preliminary results show that the proposed method can achieve an accuracy of better than 0.5 pixels in planimetry and is suitable for wide application in ortho-map production. It also has great potential for the ortho-map production of superlarge areas such as the country of China as one block. [full text] [link]
-
, Qian Li, Hongshu Lu, Xinyi Liu, Xu Huang, Chao Song, Shan Huang, Jingyi Huang.(2015) Optimized 3D Street Scene Reconstruction from Driving Recorder Image. In: Remote Sensing, Vol.7: 091-9121.
Abstract: The paper presents an automatic region detection based method to reconstruct street scenes from driving recorder images. The driving recorder in this paper is a dashboard camera that collects images while the motor vehicle is moving. An enormous number of moving vehicles are included in the collected data because the typical recorders are often mounted in the front of moving vehicles and face the forward direction, which can make matching points on vehicles and guardrails unreliable. Believing that utilizing these image data can reduce street scene reconstruction and updating costs because of their low price, wide use, and extensive shooting coverage, we therefore proposed a new method, which is called the Mask automatic detecting method, to improve the structure results from the motion reconstruction. Note that we define vehicle and guardrail regions as “mask” in this paper since the features on them should be masked out to avoid poor matches. After removing the feature points in our new method, the camera poses and sparse 3D points that are reconstructed with the remaining matches. Our contrast experiments with the typical pipeline of structure from motion (SfM) reconstruction methods, such as Photosynth and VisualSFM, demonstrated that the Mask decreased the root-mean-square error (RMSE) of the pairwise matching results, which led to more accurate recovering results from the camera-relative poses. Removing features from the Mask also increased the accuracy of point clouds by nearly 30%–40% and corrected the problems of the typical methods on repeatedly reconstructing several buildings when there was only one target building. [full text] [link]
-
Xiang Shen,, Xiao Lu, Qian Xie, Qingquan Li. (2015) An Improved Method for Transforming GPS/INS Attitude to National Map Projection Frame. In: IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, Vol.12 No.6: 1302-1306.
Abstract: Global Positioning System/Inertial Navigation System (GPS/INS) integrated navigation systems play a very important role in modern photogrammetry and laser scanning by virtue of their capability of direct measurement of high-precision position and attitude data in the WGS 84 datum. In practice, as georeferencing is often conducted in national coordinates, there is a need to transform GPS/INS data to the required national map projection frame first. This letter presents an improved coordinate-transformation-based method for the GPS/INS attitude transformation by taking the datum scale distortion and the length distortion into account. Experimental results show that the transformation errors of our improved method are on the order of magnitude of 1 × 10-5°, which can be safely ignored in aerial photogrammetric processing, whereas the maximum error of the previous coordinate-transformation-based method can be up to several 0.001°. [full text] [link]
-
Xiang Shen,, Qingquan Li. (2015) Accurate Direct Georeferencing of Aerial Imagery in National Coordinates. In: ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, Vol.105 No.3: 13-18.
Abstract: In aerial photogrammetry, data products are commonly needed in national coordinates, and, in practice, the georeferencing is often performed in the required national map projection frame directly. However, as a map projection frame is not Cartesian, some additional corrections are necessary in the georeferencing process to take account of various map projection distortions. This paper presents a new map projection correction method for the direct georeferencing of aerial images in national coordinates, which comprises of three consecutive steps: (1) a rough intersection to predict ground point coordinates in the Cartesian space; (2) calculating map projection corrections; and (3) a fine intersection. Benefiting from the explicit estimation of ground positions in the Cartesian space, our new method can directly adopt the accurate map projection distortion model that was previously developed for the direct georeferencing of airborne LiDAR data in national coordinates. Simulations show that the correction residuals of our new method are smaller by one order of magnitude than those of the previous best approach while their computational costs are at the same level, and even in an extreme scenario of 8000 m flight height above ground, the maximum error of our method is only several centimeters, which can be safely neglected in practical applications. [full text] [link]
-
Maoteng Zheng,. (2015) Self-Calibration Adjustment of CBERS-02B Long Strip Imagery. In: IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Vol.53 No.7: 3847-3854.
Abstract: Due to hardware limitations, such as the poor accuracy of its onboard Global Positioning System receiver and star tracks, the direct georeferencing accuracy of the China and Brazil Earth Resource Satellite 02B (CBERS-02B) by its onboard position and attitude measurements is less than 1000 m at times. Thus, the image data cannot be directly used in surveying applications. This paper presents a self-calibration bundle adjustment strategy to improve the georeferencing accuracy of the onboard high-resolution camera (HRC). An adequate number of automatically matched ground control points (GCPs) are used to perform the bundle adjustment. Both the systematic error compensation model and the orientation image model along with the interior self-calibration parameters are used in the bundle adjustment to eliminate the systematic errors. A self-calibration strategy is used to compensate for the time delay and integrated charge-coupled device translation and rotation errors by introducing a total of ten interior orientation parameters. The preliminary results show that the accuracy of self-calibration bundle adjustment is two pixels better than that of bundle adjustment without self-calibration, and the planimetric accuracy of the check points is about 10 m. The unusual variations of the exterior orientation parameters in some cases are eliminated after enlarging the orientation image intervals and increasing the weights of the onboard position and attitude observations. [full text] [link]
-
, Xiaodong Xiong, Maoteng Zheng. (2015) LiDAR Strip Adjustment Using Multifeatures Matched with Aerial Images. In: IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Vol.53 No.2: 976-987.

Abstract: Airborne light detecting and ranging (LiDAR) systems have been widely used for the fast acquisition of dense topographic data. Regrettably, coordinate errors always exist in LiDAR-acquired points. The errors are attributable to several sources, such as laser ranging errors, sensor mounting errors, and position and orientation system (POS) systematic errors, among others. LiDAR strip adjustment (LSA) is the solution to eliminating the errors, but most state-of-the-art LSA methods neglect the influence from POS systematic errors by assuming that the POS is precise enough. Unfortunately, many of the LiDAR systems used in China are equipped with a low-precision POS due to cost considerations. Subsequently, POS systematic errors should be also considered in the LSA. This paper presents an aerotriangulation-aided LSA (AT-aided LSA) method whose major task is eliminating position and angular errors of the laser scanner caused by boresight angular errors and POS systematic errors. The aerial images, which cover the same area with LiDAR strips, are aerotriangulated and serve as the reference data for LSA. Two types of conjugate features are adopted as control elements (i.e., the conjugate points matched between the LiDAR intensity images and the aerial images and the conjugate corner features matched between LiDAR point clouds and aerial images). Experiments using the AT-aided LSA method are conducted using a real data set, and a comparison with the three-dimensional similarity transformation (TDST) LSA method is also performed. Experimental results support the feasibility of the proposed AT-aided LSA method and its superiority over the TDST LSA method. [full text] [link]
-
, Maoteng Zheng, Xiaodong Xiong, Jinxin Xiong. (2015) Multi-strips Bundle Block Adjustment of ZY-3 Satellite Imagery by Rigorous Sensor Model. In: IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, Vol.12 No.4: 865-869.
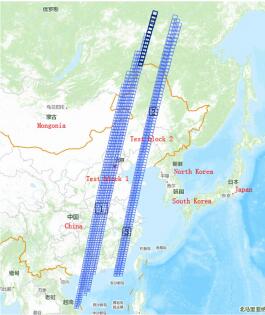
Abstract: Extensive applications of Zi-Yuan 3 (ZY-3) satellite imagery of China have commenced since its on-orbit test was finished. Most of the data are processed scene by scene with a few ground control points (GCPs) for each scene; this conventional method is mature and widely used all over the world. However, very little work has focused on its application to super large area blocks. This letter aims to study mapping applications without GCPs for a super large area, which is defined as a range of interprovincial or even nationwide areas. The automatic matching and bundle block adjustment (BBA) software developed by our research team are applied to deal with two blocks of ZY-3 three-line camera imagery which covers most of the provinces in eastern China. Our comparison analysis of different data processing methods and the geolocation accuracies of the overlapped areas between adjacent strips are presented in this letter, as well as the possibility of nationwide BBA. The preliminary test results show that multistrip BBA without GCPs can achieve accuracies of about 13-15 m in both planimetry and height, which means that nationwide BBA is considered practical and feasible. [full text] [link]
-
, Bo Wang, Zuxun Zhang, Yansong Duan, Yong Zhang, Mingwei Sun, Shunping Ji. (2014) Fully Automatic Generation of Geo-information Products with Chinese ZY-3 Satellite Imagery. In: The Photogrammetric Record, Vol.29 No.148: 383-401.

Abstract: The advantages of continuously and soundly obtaining large multidimensional, multiscale and multitemporal observation datasets from satellite remote sensing make it indispensable in building a national spatial data infrastructure. This paper introduces the ZY‐3 satellite developed in China and discusses a fully automatic data‐processing system to generate geoinformation products, such as digital elevation models (DEMs) and digital orthophotomaps (DOMs), based on ZY‐3 imagery. The key technologies of automatic geoinformation product generation, including strip image‐based bundle adjustment together with creating DEMs and DOMs, are illustrated. The accuracies of the georeferencing and automatically generated geoinformation products are also discussed. This automatic data‐processing system is shown to provide a good foundation for near real‐time derivation of such geoinformation products and for the promotion and application of Chinese domestic satellites. [full text] [link]
-
Xiaodong Xiong, , Junfeng Zhu, Maoteng Zheng. (2014) Camera Pose Determination and 3D Measurement from Monocular Oblique Images with Horizontal Right Angle Constraints. In: IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, Vol.11 No.11: 1976-1980.
Abstract: This letter introduces a novel method for camera pose determination from monocular urban oblique images. Horizontal right angles that widely exist in urban scenes are used as geometric constraints in the camera pose determination, and the proposed 3-D measurement method using a monocular image is presented and then used to check the accuracy of the recovered image's exterior orientation parameters. Compared to the available vertical-line-based camera pose determination method, our new method is more accurate. [full text] [link]
-
, Maoteng Zheng, Xu Huang, Jinxin Xiong. (2014) Bundle Block Adjustment of Airborne Three-Line Array Imagery Based on Rotation Angles. In: Sensors, Vol.14: 8189-8202.

Abstract: In the midst of the rapid developments in electronic instruments and remote sensing technologies, airborne three-line array sensors and their applications are being widely promoted and plentiful research related to data processing and high precision geo-referencing technologies is under way. The exterior orientation parameters (EOPs), which are measured by the integrated positioning and orientation system (POS) of airborne three-line sensors, however, have inevitable systematic errors, so the level of precision of direct geo-referencing is not sufficiently accurate for surveying and mapping applications. Consequently, a few ground control points are necessary to refine the exterior orientation parameters, and this paper will discuss bundle block adjustment models based on the systematic error compensation and the orientation image, considering the principle of an image sensor and the characteristics of the integrated POS. Unlike the models available in the literature, which mainly use a quaternion to represent the rotation matrix of exterior orientation, three rotation angles are directly used in order to effectively model and eliminate the systematic errors of the POS observations. Very good experimental results have been achieved with several real datasets that verify the correctness and effectiveness of the proposed adjustment models. [full text] [link]
-
, Xiang Shen. (2014) Quantitative Analysis on Geometric Size of LiDAR Footprint. In: IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, Vol.11 No.3: 701-705.
Abstract: A light detection and ranging (LiDAR) footprint is the spot area illuminated by a single laser beam, which varies with the beam direction and the regional terrain encountered. The geometric size of the LiDAR footprint is one of the most critical parameters of LiDAR point cloud data. It plays a very important role in the high-precision geometric and radiometric calibration of LiDAR systems. This letter utilizes space analytic geometry to derive LiDAR footprint equations and strictly considers laser beam attitude and terrain slope. Compared to the conventional plane geometry solution, the proposed approach is not only more rigorous in theory but also more powerful in practical applications. [full text] [link]
-
, Maoteng Zheng, Jinxin Xiong, Yihui Lu, Xiaodong Xiong. (2014) On-Orbit Geometric Calibration of ZY-3 Three-Line Array Imagery With Multistrip Data Sets. In: IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Vol.52 No.1: 224-234.
Abstract: ZY-3, which was launched on January 9, 2012, is the first stereo mapping satellite in China. The initial accuracy of direct georeferencing with the onboard three-line camera (TLC) imagery is low. Sensor geometric calibration with bundle block adjustment is used to improve the georeferencing accuracy. A new on-orbit sensor calibration method that can correct the misalignment angles between the spacecraft and the TLC and the misalignment of charge-coupled device is described. All of the calibration processes are performed using a multistrip data set. The control points are automatically matched from existing digital ortho map and digital elevation model. To fully evaluate the accuracy of different calibration methods, the calibrated parameters are used as input data to conduct georeferencing and bundle adjustment with a total of 19 strips of ZY-3 TLC data. A systematic error compensation model is introduced as the sensor model in bundle adjustment to compensate for the position and attitude errors. Numerous experiments demonstrate that the new calibration model can largely improve the external accuracy of direct georeferencing from the kilometer level to better than 20 m in both plane and height. A further bundle block adjustment with medium-accuracy ground control points (GCPs), using these calibrated parameters, can achieve external accuracy of about 4 m in plane and 3 m in height. Higher accuracy of about 1.3 m in plane and 1.7 m in height can be achieved by bundle adjustment using high-accuracy GCPs. [full text] [link]
-
, Xiang Shen. (2013) Direct georeferencing of airborne LiDAR data in national coordinates. In: ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, Vol.84: 43-51.
Abstract: The topographic mapping products of airborne light detection and ranging (LiDAR) are usually required in the national coordinates (i.e., using the national datum and a conformal map projection). Since the spatial scale of the national datum is usually slightly different from the World Geodetic System 1984 (WGS 84) datum, and the map projection frame is not Cartesian, the georeferencing process in the national coordinates is inevitably affected by various geometric distortions. In this paper, all the major direct georeferencing distortion factors in the national coordinates, including one 3D scale distortion (the datum scale factor distortion), one height distortion (the earth curvature distortion), two length distortions (the horizontal-to-geodesic length distortion and the geodesic-to-projected length distortion), and three angle distortions (the skew-normal distortion, the normal-section-to-geodesic distortion, and the arc-to-chord distortion) are identified and demonstrated in detail; and high-precision map projection correction formulas are provided for the direct georeferencing of the airborne LiDAR data. Given the high computational complexity of the high-precision map projection correction approach, some more approximate correction formulas are also derived for the practical calculations. The simulated experiments show that the magnitude of the datum scale distortion can reach several centimeters to decimeters for the low (e.g., 500 m) and high (e.g., 8000 m) flying heights, and therefore it always needs to be corrected. Our proposed practical map projection correction approach has better accuracy than Legat’s approach,1 but it needs 25% more computational cost. As the correction accuracy of Legat’s approach can meet the requirements of airborne LiDAR data with low and medium flight height (up to 3000 m above ground), our practical correction approach is more suitable to the high-altitude aerial imagery. The residuals of our proposed high-precision map projection correction approach are trivial even for the high flight height of 8000 m. It can be used for the theoretical applications such as the accurate evaluation of different GPS/INS attitude transformation methods to the national coordinates. [full text] [link]
-
, Kun Hu, Zuxun Zhang, Tao Ke, Shan Huang. (2013) Precise Calibration of a Rotation Photogrammetric System. In: Geo-spatial Information Science, Vol.16 No.2: 69-74.
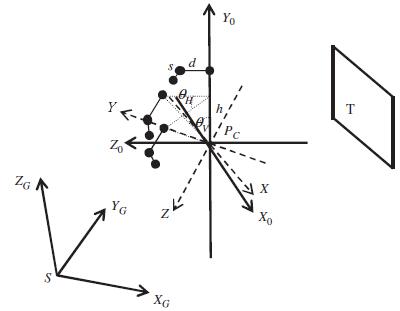
Abstract: Rotation photogrammetric systems are widely used for 3D information acquisition, where high-precision calibration is one of the critical steps. This study first shows how to derive the rotation model and deviation model in the object space coordinate system according to the basic structure of the system and the geometric relationship of the related coordinate systems. Then, overall adjustment of multi-images from a surveying station is employed to calibrate the rotation matrix and the deviation matrix of the system. The exterior orientation parameters of images captured by other surveying stations can be automatically calculated for 3D reconstruction. Finally, real measured data from Wumen wall of the Forbidden City is employed to verify the performance of the proposed calibration method. Experimental results show that this method is accurate and reliable and that a millimetre level precision can be obtained in practice. [full text] [link]
-
, Xiang Shen. (2013) Approximate Correction of Length Distortion for Direct Georeferencing in Map Projection Frame. In: IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, Vol.10 No.6: 1419-1423.
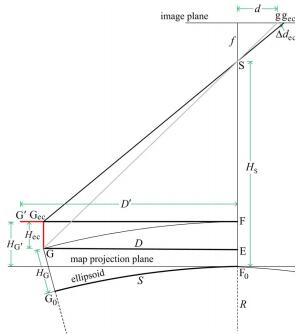
Abstract: Many geometric distortions, such as earth curvature distortion and length distortion, exist in the map projection frame. Therefore, in aerial photogrammetry, if direct georeferencing is performed in the map projection frame, the crucial work becomes compensating for the effect of the various geometric distortions. This letter mainly focuses on length distortion and proposes two new correction approaches: the changing image coordinates method and the changing object coordinates method. The experimental results show that the changing object coordinates method is less influenced by terrain fluctuation, and its correction accuracy is therefore commonly higher than the changing image coordinates method as well as two existing approaches (i.e., the changing flight height method and the changing focal length method). [full text] [link]
-
, Liwen Lin, Maoteng Zheng, Jinxin Xiong. (2013) Combined Bundle Block Adjustment with Spaceborne Linear Array and Airborne Frame Array Imagery. In: The Photogrammetric Record, Vol.28 No.145: 162-177.
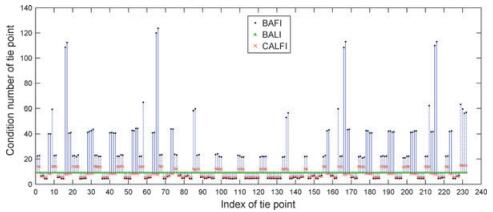
Abstract: The integration of multi‐source earth observation data has become one of the most important developments in photogrammetry. A combined adjustment with linear array and frame array imagery (CALFI) is established in this paper. The mathematical model of CALFI is based on the conventional single‐source bundle adjustment. A revised recursive partitioning technique is utilised to solve the large normal matrix of CALFI; the orientation parameters of the linear array imagery are arranged at the border of the reduced normal matrix to save both memory and computation time. The experimental results on simulated data show that both the accuracy and the condition index of the CALFI model are superior to the conventional bundle adjustment model with either linear array or frame array imagery separately due to the higher redundancy. [full text] [link]
-
, Kun Hu, Rongyong Huang. (2012) Bundle Adjustment with Additional Constraints Applied to Imagery of the Dunhuang Wall Paintings. In: ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, Vol.72 No.1: 113-120.
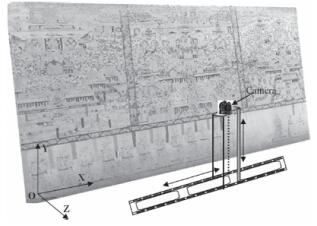
Abstract: In the digital conservation of the Dunhuang wall painting, bundle adjustment is a critical step in precise orthoimage generation. The error propagation of the adjustment model is accelerated because the near-planar photographic object intensifies correlation of the exterior orientation parameters and the less than 60% forward overlap of adjacent images weakens the geometric connection of the network. According to the photographic structure adopted in this paper, strong correlation of the exterior orientation parameters can be verified theoretically. In practice, the additional constraints of near-planarity and exterior orientation parameters are combined with bundle adjustment to control the error propagation. The positive effects of the additional constraints are verified by experiments, which show that the introduction of weighted observation equations into bundle adjustment contributes a great deal to the theoretical and actual accuracies of the unknowns as well as the stability of the adjustment model. [full text] [link]
-
, Xiaodong Xiong, Xiang Shen, Zheng Ji.(2012) Bundle Block Adjustment of Weakly Connected Aerial Imagery. In: Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, Vol.78 No.9: 983-989.
Abstract: In aerial photogrammetry of island and reef areas, traditional aerial triangulation cannot be performed because many images in the block are partially or even completely covered by water, and thus there are not enough tie points among adjacent images. To solve this problem, an effective algorithm of position and orientation system (POS) integrated bundle block adjustment is proposed. The exterior orientation parameters of each image are modeled as functions of corresponding POS observations and their estimated systematic errors. A POS integrated bundle adjustment model is designed with the purpose of effectively eliminating the systematic errors of inertial measurement unit observations. Experimental results of three sets of island aerial images show that the proposed approach can compensate for the systematic errors of POS observations effectively. The topo-graphic mapping requirements of hilly terrain at 1:2 000 scale can be fulfilled, provided that at least one ground control point is used in the bundle adjustment. [full text] [link]
-
, Yihui Lu, Lei Wang, and Xu Huang. (2012) A New Approach on Optimization of the Rational Function Model of High Resolution Satellite Imagery. In: IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, Vol.50 No.7: 2758-2764.
Abstract: Overparameterization is one of the major problems that the rational function model (RFM) faces. A new approach of RFM parameter optimization is proposed in this paper. The proposed RFM parameter optimization method can resolve the ill-posed problem by removing all of the unnecessary parameters based on scatter matrix and elimination transformation strategies. The performances of conventional ridge estimation and the proposed method are evaluated with control and check grids generated from Satellites d'observation de la Terre (SPOT-5) high-resolution satellite data. Experimental results show that the precision of the proposed method, with about 35 essential parameters, is 10% to 20% higher than that of the conventional model with all 78 parameters. Moreover, the ill-posed problem is effectively alleviated by the proposed method, and thus, the stability of the estimated parameters is significantly improved. [full text] [link]
-
, Xu Huang, Xiangyun Hu, Fangqi Wan, Liwen Lin. (2011) Direct Relative Orientation with Four Independent Constraints. In: ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, Vol.66 No.6: 809-817.

Abstract: Relative orientation based on the coplanarity condition is one of the most important procedures in photogrammetry and computer vision. The conventional relative orientation model has five independent parameters if interior orientation parameters are known. The model of direct relative orientation contains nine unknowns to establish the linear transformation geometry, so there must be four independent constraints among the nine unknowns. To eliminate the influence of over parameterization of the conventional direct relative orientation model, a new relative orientation model with four independent constraints is proposed in this paper. The constraints are derived from the inherent orthogonal property of the rotation matrix of the right image of a stereo pair. These constraints are completely new as compared with the known literature. The proposed approach can find the optimal solution under least squares criteria. Experimental results show that the proposed approach is superior to the conventional model of direct relative orientation, especially at low altitude and close range photogrammetric applications. [full text] [link]
-
, Binghua Hu, Jianqing Zhang. (2011) Relative Orientation Based on Multi-features. In: ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, Vol.66 No.5: 700-707.

Abstract: In digital photogrammetry, corresponding points have been widely used as the basic source of information to determine the relative orientation parameters among adjacent images. Sometimes, though, the conventional relative orientation process cannot be precisely implemented due to the accumulation of random errors or in the case of inadequate corresponding points. A new relative orientation approach with multiple types of corresponding features, including points, straight lines, and circular curves, is proposed in this paper. The origin of the model coordinate system is set at the projection center of the first image of a strip, and all of the exterior orientation parameters, except and ω of the first image, are set at zero. The basic models of relative orientation with corresponding points, straight lines, and circular curves are discussed, and the general form of a least squares adjustment model for relative orientation based on multi-features is established. Our experimental results show that the proposed approach is feasible and can achieve more reliable relative orientation results than the conventional approach based on corresponding points only. [full text] [link]
-
, Zuxun Zhang, Mingwei Sun, Tao Ke. (2011) Precise Orthoimage Generation of Dunhuang Wall Painting. In: Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, Vol.77 No.6: 631-640.
Abstract: Wall painting plays an important role in the culture relics of the Mogao Caves in Dunhuang, P.R. China. A novel approach of generating a high-resolution orthoimage of the wall painting is proposed. Since the photographic object is nearly flat and also the forward overlap between adjacent images is smaller than 60 percent, the main difficulty to be resolved is the high correlation problem among the unknowns. Improved models of relative orientation and bundle adjustment with virtual constraints have been developed to resolve the high correlation problem. A Voronoi diagram of projective footprints is applied to automatically determine the mosaic lines of ortho-rectified images. The color quality of the generated orthoimage is improved through global minimization of the color differences among overlapped images. The experimental results show that the proposed approach has great potential for conservation of wall paintings with sub-millimeter to millimeter precision. [full text] [link]
-
, Jinxin Xiong, Lijuan Hao. (2011) Photogrammetric Processing of Low-altitude Images Acquired by Unpiloted Aerial Vehicles. In: The Photogrammetric Record, Vol.26 No.134: 190-211.

Abstract: Low‐altitude images acquired by unpiloted aerial vehicles have the advantages of high overlap, multiple viewing angles and very high ground resolution. These kinds of images can be used in various applications that need high accuracy or fine texture. A novel approach is proposed for parallel processing of low‐altitude images acquired by unpiloted aerial vehicles, which can automatically fly according to predefined flight routes under the control of an autopilot system. The general overlap and relative rotation angles between two adjacent images are estimated by overall matching with an improved scale‐invariant feature transform (SIFT) operator. Precise conjugate points and relative orientation parameters are determined by a pyramid‐based least squares image matching strategy and the relative orientation process. Bundle adjustment is performed with automatically matched conjugate points and interactively measured ground control points. After this aerial triangulation process the high‐resolution images can be used to advantage in obtaining precise spatial information products such as digital surface models, digital orthophotomaps and 3D city models. A parallel processing strategy is introduced in this paper to improve the computational time of the photogrammetric process. Experimental results show that the proposed approaches are effective for processing low‐altitude images, and have high potential for the acquisition of spatial information at large mapping scales, with rapid response and precise modelling in three dimensions. [full text] [link]
-
Zuxun Zhang, , Tao Ke, Dahai Guo. (2009) Photogrammetry for First Response in Wenchuan Earthquake. In: Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, Vol.75 No.5: 510-513.
Abstract: To inspect the damages caused by the Wenchuang earthquake on May 12, 2008, aerial photography was practiced in an unconventional manner. The f ight was largely irregular, along the roads, in cities and towns in order to obtain the f rst-time damage information about main roads, bridges and other transportation infrastructure . Hovering f ight is necessary to get more ground information about residential areas when the plane is over the city. All this challenges for advanced techniques to process such collected images in a timely manner. Some key algorithms and data-processing mechanisms in conventional practices should be upgraded to meet this need. This paper mainly focuses on the rapid data processing and applications of mass unconventional aerial images in Wenchuan earthquake relief and emergency response. [full text] [link]
-
Zuxun Zhang, , Jianqing Zhang. (2008) Photogrammetric Modelling of Linear Features with Generalized Point Photogrammetry. In: Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, Vol.74 NO.9: 1119-1129.

Abstract: Most current digital photogrammetric workstations are based on feature points. Curved features are quite difficult to be modeled because they cannot be treated as feature points. The focus of the paper is on the photogrammetric modeling of space linear features. In general, lines and curves can be represented by a series of connected points, so called, generalized points in the paper. Different from all existing models, only one collinearity equation is used for each point on the linear curve, which makes the mathematical model very simple. Hereby, the key of generalized point photogrammetry is that all kinds of features are treated as generalized points to use either x or y collinearity equation. A significant difference between generalized point photogrammetry and conventional point photogrammetry is that image features are not necessarily exact conjugates. The exact conjugacy between image features and/or the correspondence between space and image feature are established during bundle block adjustment. Photogrammetric modeling of several space linear features is discussed. Sub-pixel precision has been achieved for both exterior orientation and 3D modeling of linear features, which verifies the correctness and effectiveness of the proposed approach. [full text] [link]
-
, Zuxun Zhang, Jianqing Zhang. (2006) Automatic Measurement of Industrial Sheetmetal Parts with CAD Data and Non-metric Image Sequence. In: Computer Vision and Image Understanding, Vol. 102 No.1: 52-59.
Abstract: A novel approach for three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction and measurement of industrial sheetmetal parts with computer aided design (CAD) data and non-metric image sequence is proposed. The purpose of our approach is to automatically reconstruct and measure the producing imprecision or deformations of industrial parts that are mainly composed of line segments, circles, connected arcs and lines. Principles of two-dimensional (2D) and one-dimensional (1D) least squares template matching to extract precise lines and points are presented. Hybrid point-line photogrammetry is adopted to obtain accurate wire frame model of industrial parts. Circles, arcs, and lines connected to each other on the part are reconstructed with direct object space solution according to known camera parameters. The reconstructed CAD model can be used for visual measurement. Experimental results of several parts are very satisfying. They show that the proposed approach has a promising potential in automatic 3D reconstruction and measurement of widely existed industrial parts mainly composed of lines, circles, connected arcs and lines. [full text] [link]
-
, Christian Heipke, Matthias Butenuth, Xiangyun Hu. (2006) Automatic Extraction of Wind Erosion Obstacles by Integration of GIS Data, DSM and Stereo Images. In: International Journal of Remote Sensing, Vol.27 No.8: 1677-1690.

Abstract: Integrating multiple data sources is a very important strategy to obtain relevant solutions in geo‐scientific analysis. This paper mainly deals with the integration of Geographical Information System (GIS) data, stereo aerial imagery and a Digital Surface Model (DSM) to extract wind erosion obstacles (namely tree rows and hedges) in open landscapes. Different approaches, such as image segmentation, edge extraction, linking, grouping and 3‐dimensional verification with the DSM, are combined to extract the objects of interest. Experiments show that most wind erosion obstacles can be successfully extracted by the developed system. [full text] [link]
-
, Zuxun Zhang, Jianqing Zhang, Jun Wu. (2005) 3D Building Modelling with Digital Map, LIDAR Data and Video Image Sequences. In: The Photogrammetric Record, Vol.20 NO.111: 285-302.

Abstract: Three‐dimensional (3D) reconstruction and texture mapping of buildings or other man‐made objects are key aspects for 3D city landscapes. An effective coarse‐to‐fine approach for 3D building model generation and texture mapping based on digital photogrammetric techniques is proposed. Three video image sequences, two oblique views of building walls and one vertical view of building roofs, acquired by a digital video camera mounted on a helicopter, are used as input images. Lidar data and a coarse two‐dimensional (2D) digital vector map used for car navigation are also used as information sources. Automatic aerial triangulation (AAT) suitable for a high overlap image sequence is used to give initial values of camera parameters of each image. To obtain accurate image lines, the correspondence between outlines of the building and their line features in the image sequences is determined with a coarse‐to‐fine strategy. A hybrid point/line bundle adjustment is used to ensure the stability and accuracy of reconstruction. Reconstructed buildings with fine textures superimposed on a digital elevation model (DEM) and ortho‐image are realistically visualised. Experimental results show that the proposed approach of 3D city model generation has a promising future in many applications. [full text] [link]
-
. (2005) Automatic Inspection of Industrial Sheetmetal Parts with Single Non-metric CCD Camera. In: Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence, No.3584: 654-661.
Abstract: A novel approach for three-dimensional reconstruction and inspection of industrial parts with image sequence acquired by single non-metric CCD camera is proposed. The purpose of the approach is to reconstruct and thus inspect the producing imprecision (of deformation) of industrial sheetmetal parts. Planar control grid, non-metric image sequence and CAD-designed data are used as information sources. Principles of least squares template matching to extract lines and points from the imagery are presented. Hybrid point-line photogrammetry is adopted to obtain the accurate wire frame model. Circles, connected arcs and lines on the part are reconstructed with direct object space solution. The reconstructed CAD model can be used for inspection or quality control. Experimental results are very satisfying. [full text] [link]
-
, Zuxun Zhang, Jianqing Zhang. (2004) Deformation Visual Inspection of Industrial Parts with Image Sequence. In: Machine Vision and Applications, Vol.15 No.3: 115-120.
Abstract: A new approach to reconstructing and inspecting the deformation of industrial parts, especially sheetmetal parts based on CAD-designed data and hybrid point-line bundle adjustment with image sequence, is proposed. Nonmetric image sequence and CAD-designed data of parts are used as the source of information. The strategy of our approach is to reconstruct and inspect deformations of parts automatically with image points and line segments extracted from the images. Basic error equation of line photogrammetry and its modified form are addressed in detail. It is shown that when a certain proper weight is selected, adjustment by condition equations and adjustment by observation equations are equivalent for line photogrammetry. A novel hybrid point-line bundle adjustment algorithm is used to reconstruct industrial parts. The proposed hybrid adjustment model can be used in various 3D reconstruction applications of objects mainly composed of points and lines. The developed inspection system is tested with true image data acquired by a CCD camera, and the results are very satisfying. [full text] [link]
-
, Zuxun Zhang, Jianqing Zhang. (2003) Flexible Planar-scene Camera Calibration Technique. In: Wuhan University Journal of Natural Science, Vol.8 No.4: 1090-1096.
Abstract: A flexible camera calibration technique using 2D-DLT and bundle adjustment with planar scenes is proposed. The equation of principal line under image coordinate system represented with 2D-DLT parameters is educed using the correspondence between collinearity equations and 2D-DLT. A novel algorithm to obtain the initial value of principal point is put forward. Proof of Critical Motion Sequences for calibration is given in detail. The practical decomposition algorithm of exterior parameters using initial values of principal point, focal length and 2D-DLT parameters is discussed elaborately. Planar-scene camera calibration algorithm with bundle adjustment is addressed. Very good results have been obtained with both computer simulations and real data calibration. The calibration result can be used in some high precision applications, such as reverse engineering and industrial inspection. [full text] [link]
-
, Jingnan Liu. (2002) Combined GPS/GLONASS Data Processing. In: Geo-Spatial Information Science, Vol.15 No.4: 32-36.
Abstract: To obtain the GLONASS satellite position at an epoch other than reference time, the satellite's equation of motion has to be integrated with broadcasting ephemerides. The iterative detecting and repairing method of cycle slips based on triple difference residuals for combined GPS/GLONASS positioning and the iterative ambiguity resolution approach suitable for combined post processing positioning are discussed systematically. Experiments show that millimeter accuracy can be achieved in short baselines with a few hours' dual frequency or even single frequency GPS/GLONASS carrier phase observations, and the precision of dual frequency observations is distinctly higher than that of single frequency observations. [full text] [link]
-
, Zemin Wang. (2002) Analysis and Solutions of Errors on GPS/GLONASS Positioning. In: Geo-Spatial Information Science, Vol.15 No.2: 6-13.
Abstract: This paper focuses mainly on the major errors and their reduction approaches pertaining to combined GPS/GLONASS positioning. To determine the difference in the time reference systems, different receiver clock offsets are introduced with respect to GPS and GLONASS system time. A more desirable method for introducing a independent unknown parameter of fifth receiver, which can be canceled out when forming difference measurements, is dicussed. The error of orbit integration and the error of transformation parameters are addressed in detail. Results of numerical integration are given. To deal with the influence of ionospheric delay, a method for forming dual-frequency ionospheric free carrier phase measurements is detailed. [full text] [link]
-
Zhaoxi Yue, , Yansong Duan, Lei Yu. (2018) DEM Assisted Shadow Detection and Topography Correction of Satellite Remote Sensing Images in Mountainous Area. In: Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, Vol. 47, No. 1: 113-122.
DEM辅助的卫星光学遥感影像山体阴影检测与地形辐射校正
Abstract: A shadow detection and topography correction method based on DEM is proposed.Firstly,characteristic method is used to detect the shadow area in the satellite imagery.Then the shady slope and cast shadow area can be detected by model method using DEM data.The shadow is divided into 8 categories with the cause of formation.And then,the compensation method of shadow area and topography correction model are used to correct the optical remote sensing satellite imagery.The results suggest that the proposed method can recover the shadow area information effectively and weaken the effect of terrain. [full text] [link]
-
Qian Li, , Hongshu Lu, Xinyi Liu. (2018) Detection of Pedestrian Crossings with Hierarchical Learning Classifier from Multi-angle Low Altitude Images. In: GEOMATICS AND INFORMATION SCIENCE OF WUHAN UNIVERS, Vol. 43, No. 1: 46-52.
基于错误式学习的低空影像人行横道多角度自动识别
Abstract: This paper proposes a new training method for feature-based iterative hierarchical learning classifiers. It can be used to detect pedestrian crossings from multi-angle low altitude images. The training procedure and the method for merging multi-angle detection results are introduced in this paper. The performance of the classifier was evaluated based on random testing results. Experimental results from several datasets show that the iterative classifier has higher correctness, lower missing rate and lower error rate than the general classifier. Furthermore, the proposed method will not reduce the detection speed. [full text] [link]
-
Maoteng Zheng, , Junfeng Zhu, Xiaodong Xiong, Shunping Zhou. (2017) A Fast and Effective Block Adjustment Method with Big Data. In: Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, Vol.46, No.2: 188-197(10).
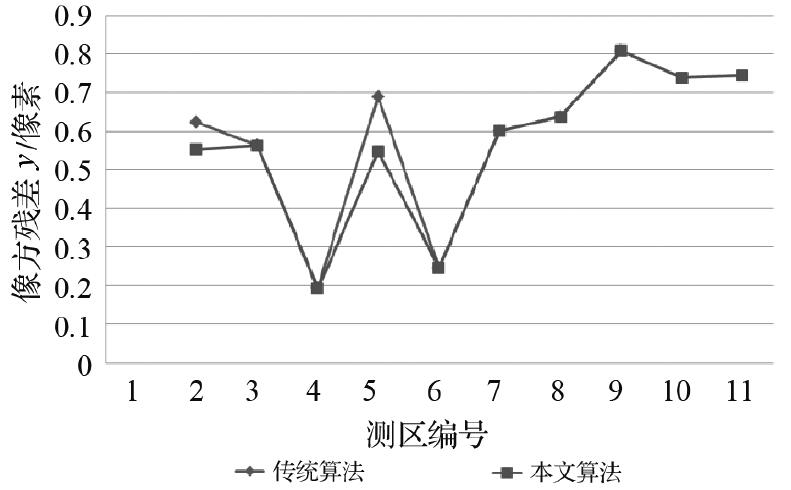
一种快速有效的大数据区域网平差方法
Abstract: To deal with multi-source, complex and massive data in photogrammetry, and solve the high memory requirement and low computation efficiency of irregular normal equation caused by the randomly aligned and large scale datasets, we introduce the preconditioned conjugate gradient combined with inexact Newton method to solve the normal equation which do not have strip characteristics due to the randomly aligned images. We also use an effective sparse matrix compression format to compress the big normal matrix, a brand new workflow of bundle adjustment is developed. Our method can avoid the direct inversion of the big normal matrix, the memory requirement of the normal matrix is also decreased by the proposed sparse matrix compression format. Combining all these techniques, the proposed method can not only decrease the memory requirement of normal matrix, but also largely improve the efficiency of bundle adjustment while maintaining the same accuracy as the conventional method. Preliminary experiment results show that the bundle adjustment of a dataset with about 4500 images and 9 million image points can be done in only 15 minutes while achieving sub-pixel accuracy. [full text] [link]
-
Lei Yu, , Mingwei Sun, Xinyu Zhu. (2016) Fusion of Cloudy Optical Satellite Imagery by Cloud Detection and High Pass Filtering. In: Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, Vol.41 No.9: 1160-1167.

联合云检测与高通滤波的含云影像融合方法
Abstract: Noise from clouds is a common problem in optical satellite image processing. The high pass filter (HPF) fusion method is analyzed as a way to estimate the influence of cloud noise during image fusion. An approach combining cloud detection with HPF is introduced that refines the results of image fusion containing clouds. A, NIR/R-OTSU cloud detection approach is employed for real-time cloud detection, thus areas covered by clouds can be identified. A local optimization strategy is adopted in image fusion with HPF in cloudless blocks to get the fused image. Merged multispectral and panchromatic iZY-3 satellite image results show that the algorithm discussed in this paper performs better than HPF, IHS transform and Pansharp methods for merging images with clouds. [full text] [link]
-
Wenqing Feng, . (2016) Object-oriented Change Detection for Remote Sensing Images Based on Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation. In: Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, Vol.41 No.9: 875-881.

利用模糊综合评判进行面向对象的遥感影像变化检测
Abstract: In the process of object-oriented change detection, the accuracy of the final result is directly related to the change threshold. Aiming at this problem, this paper presents a novel object-oriented change detection method using fuzzy comprehensive evaluation. Firstly, multi-scale segmentation is used to obtain initial objects; then, optional features for each object are chosen. Several criteria, such as objects change vector analysis, Chi-square transformation, the similarity of vector, and correlation coefficient, are treated as factors to get the “synthetic inter-layer logical values” of the fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model. The fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model is used to decide whether the target object has changed or not. Finally, the result of fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model is compared with the result of each single “inter-layer logical value” that using OTSU threshold segmentation. Based on this theory, experiments are done with SPOT5 multi-spectral remote sensing imagery. The experimental results illustrate that the model proposed can integrate the spectral and texture features and also overcome the defects caused by using single criteria. The fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model is proved to outperform other methods. [full text] [link]
-
Kai Tan, , Xin Tong, Yifei Kang. (2016) Automatic Cloud Detection for Chinese High Resolution Remote Sensing Satellite Imagery. In: Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, Vol.45 No.5: 581-591.
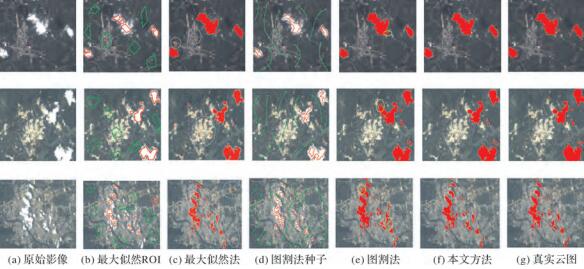
国产高分辨率遥感卫星影像自动云检测
Abstract: Cloud detection is always an arduous problem in satellite imagery processing, especially the thin cloud which has the similar spectral characteristics as ground surfacehas long been the obstacle of the production of imagery product. In this paper, an automatic cloud detection method for Chinese high resolution remote sensing satellite imagery is introduced to overcome this problem.Firstly, the image is transformed from RGB to HIS color space by an improved color transformation model. The basic cloud coverage figure is obtained by using the information of intensity and saturation,followed by getting the modified figure with the information of near-infrared band and hue. Methods of histogram equalization and bilateral filtering, combined with conditioned Otsu thresholding are adopted to generate texture information. Then the cloud seed figureis obtained by using texture information to eliminate the existed errors in the modified figure. Finally, cloud covered areas are accurately extracted by integration of intensity information from the HIS color space and cloud seed figure. Compared to the detection results of other automatic and interactive methods, the overall accuracy of our proposed method achieves nearly 10% improvement, and it is capable of improving the efficiency of cloud detection significantly. [full text] [link]
-
Xiang Wang, , Shan Huang, Xiongwei Xie. (2016) Bandwidth Optimization of Normal Equation Matrix in Bundle Block Adjustment in Multi-baseline Rotational Photography. In: Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, Vol.45 No.2: 170-177.
旋转多基线摄影光束法平差法方程矩阵带宽优化
Abstract: A new bandwidth optimization method of normal equation matrix in bundle block adjustment in multi-baseline rotational close range photography by image index re-sorting is proposed. The equivalent exposure station of each image is calculated by its object space coverage and the relationship with other adjacent images. Then, according to the coordinate relations between equivalent exposure stations, new logical indices of all images are computed, based on which, the optimized bandwidth value can be obtained. Experimental results show that the bandwidth determined by our proposed method is significantly better than its original value, thus the operational efficiency, as well as the memory consumption of multi-baseline rotational close range photography in real-data applications, is optimized to a certain extent. [full text] [link]
-
Xu Huang, , Jinglin Yang, Lianwei Ma, Xiaodong Xiong, Rongyong Huang. (2016) Closed-form Solution to Space Resection Based on Homography Matrix. In: Journal of Remote Sensing. Vol.20 No.3: 431-440.
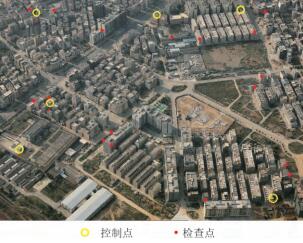
单应性几何下的后方交会直接解法
Abstract: Space resection is the method of acquiring the exterior orientation parameters of a camera based on three ground control points (GCPs) at least and the corresponding image points. The traditional least squares method of space resection needs good initial values of exterior orientation parameters. However, good initial values are difficult to obtain in the oblique photogrammetry condition. The objective of this study is to compute accurate exterior orientation parameters automatically to provide good initial values for the least squares method of space resection. Solving the space resection problem needs three GCPs and the corresponding image points at least. This study initially starts from three GCPs and then derives a direct solution model of space resection. The three GCPs must be coplanar and the corresponding image points must also be coplanar. Thus, the homography matrix can be used to describe the geometric relationship between a set of coplanar points and another set of coplanar points. This study transforms the collinearity equation into a homography matrix model and derives two constraints based on the orthogonality of the rotation matrix. When only three GCPs exist, the space resection problem can be transformed into a set of binary quadratic equations. The binary quadratic equations have four solutions at most. An additional GCP is necessary to decide the unique solution. When three ground control points exist, the unique solution can be directly computed based on a set of linear equations, which are derived from the homography matrix model. After computing the homography matrix solution, the exterior orientation parameters can be obtained using the relationship between the homography matrix and collinearity equation. Three experiments tested the effectiveness and reliability of the proposed method... [full text] [link]
-
Wenqing Feng, . (2015) Object-oriented Change Detection for Remote Sensing Images Based on Multi-scale Fusion. In: Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, Vol.44 No.10: 1142-1151.
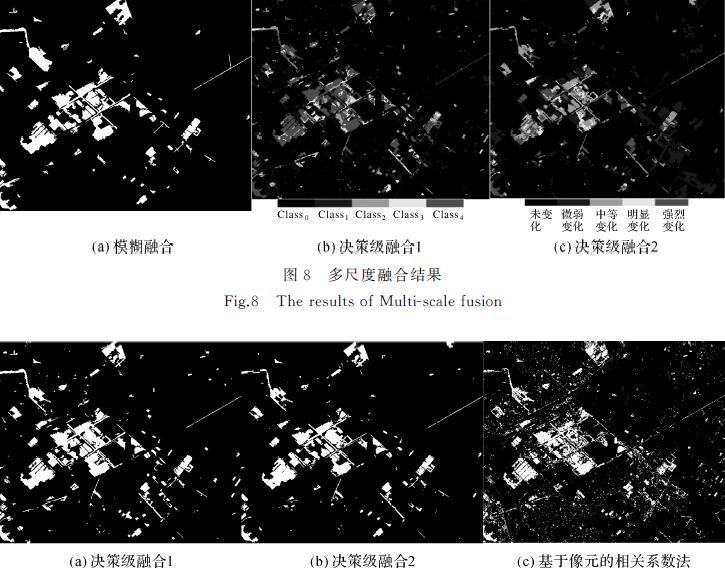
利用多尺度融合进行面向对象的遥感影像变化检测
Abstract: In the process of object-oriented change detection, the determination of the optimal segmentation scale is directly related to the subsequent change information extraction and analysis. Aiming at this problem, this paper presents a novel object-level change detection method based on multi-scale segmentation and fusion. First of all, the fine to coarse segmentation is used to obtain initial objects which have different sizes; then, according to the features of the objects, the method of change vector analysis is used to obtain the change detection results of various scales. In order to improve the accuracy of change detection, this paper introduces fuzzy fusion and two kinds of decision level fusion methods to get the results of multi-scale fusion. Based on these methods, experiments are done with SPOT5 multi-spectral remote sensing imagery. Compared with pixel-level change detection methods, the overall accuracy of our method has been improved by nearly 10%, and the experimental results prove the feasibility and effectiveness of the fusion strategies. [full text] [link]
-
Daifeng Peng, , Xiaodong Xiong. (2015) 3D Building Change Detection by Combining LiDAR Point Clouds and Aerial Imagery. In: Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, Vol.40 No.4: 462-468.
结合LiDAR点云和航空影像的建筑物三维变化检测
Abstract: 针对传统建筑物变化检测方法没有考虑高程信息的缺点,提出了一种结合LiDAR点云数据和航空影像的建筑物三维变化检测方法,可同时提取建筑物高程变化信息和面积变化信息。首先将不同时期LiDAR点云分别生成数字表面模型(DSM);然后对不同时期的DSM进行差值、滤波和形态学操作得到DSM变化区,并根据共线方程将其反投影到航空影像中,再使用航空影像的光谱、纹理等信息排除树木等伪变化区的干扰;最后计算高程变化值和面积变化值。试验结果表明该方法能定量地提取高程和面积变化信息,提供更加全面准确的建筑物变化信息。 [full text] [link]
-
, Xu Huang, Xinhui Huang, Xiaodong Xiong. (2015) Relative Orientation based on Intersecting Lines. In: Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, Vol.40 No.3: 303-307.

基于相交直线的相对定向方法
Abstract: In this paper,a new relative orientation algorithm based on intersecting lines is proposed. Relative orientation parameters are obtained with the intersection equations of the extracted corresponding intersecting lines.The algorithm needs no corresponding points and can be used to solve the problem of relative orientation lacking corresponding points.Experiments with aerial images,close-range images,and oblique images show that the proposed algorithm can get robust results. Relative orientation results are more accurate and robust when combining the proposed algorithm and the traditional relative orientation method using corresponding points. [full text] [link]
-
, Bo Wang, Qi Chen, Zheng Ji. (2014) Automatic Extraction Algorithm of Mark Centers in Close-range Photogrammetry. In: Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), Vol.42 No.8: 1261-1266.

影像匹配粗差的局部矢量面元剔除方法
Abstract: 提出了一种针对不定形状近景摄影测量标志中心的自动提取算法. 结合近景摄影测量的工程实践, 在控制信息预测的基础上实现自适应Canny 算子提取标志边缘, 利用边缘提取结果自动聚类的方法重建标志边缘. 以北京故宫午门和武汉大学校园升旗台建筑测量工程为例说明该方法能够大大减少标志量测的工作量... [full text] [link]
-
Haiqing He, , Shengxiang Huang. (2014) Phase Correlation Supported Low Altitude Images Matching with Repeated Texture. In: Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, Vol.39 No.10: 1204-1207.
相位相关法辅助的重复纹理区低空影像匹配
Abstract: Low altitude image matching with repeated texture may have a small amount of corresponding points or beunsuccessful because of ambiguous matching.To solve the problem aphase correlation method supportes low altitude aerial image matching with re peated texture is proposed.The method estimates the traversal range of corresponding points including translation rotation and scale space.The traversal range is estimated by a cross -power spectrum of the image Fourier transform and a complex con jugate of another image Fourier transform.Next Harris-Laplace scale space is estimated by the scale traversal range and corners detection.Thencorresponding point matching is a chieved by a correlation coefficient and epipolar constraint.The experimental results show that the method may be reliable and practical for low altitude images matching with a repeated textureand obtains enough and well-distributed corresponding points [full text] [link]
-
, Jinxin Xiong, Lei Yu, Xiao Ling. (2014) Automatic Matching for Optical Imagery from Domestic Satellites Based on Rigorous Sensor Model. In: Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, Vol.39 No.8: 897-900.
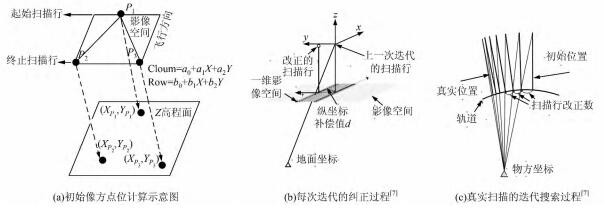
严密定位模型辅助的国产卫星影像匹配
Abstract: An image matching method based on a rigorous orientation model is presented that exploitsthe characteristics of optical imagery acquired from domestic satellites from different sensors.Firstly,this paper improves the method for scan line iterative search on the basis of the existing methods,andproposes the rapid correspondence prediction method.Next,with the help of the global SRTM(Shut-tle Radar Topography Mission)data,the approximate epipolar line is constructed by projection track-ing.The geometric and radiometric deformation in the matching window is eliminated by the correc-tion of local distortion.At last,in original level,the MPGC algorithm is adopted to refine the matc-hing results.This paper proposes a matching algorithm based on the geometric correction of the facetand the matching growth algorithm of a control network,which improves matching accuracy and thedistribution of the matching points.A test with imagery data from the TH1、ZY02Cand ZY3satellitesshowed that the proposed method can combine the characteristics of the optical imagery acquired fromdomestic satellites,and yield multi-source image matching from multi-source sensors.A well distribu-ted set of matching points can be obtained. [full text] [link]
-
, Bo Wang, Xu Huang, Yansong Duan. (2014) Eliminating of Image Matching Gross Errors Based on Local Vector Field. In: Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, Vol.43 No.7: 717-723.

影像匹配粗差的局部矢量面元剔除方法
Abstract: This paper proposes a method that can be applied to eliminating gross errors in image matching. The whole process can be divided into three steps. Firstly,the systematic difference is removed. Then triangulated irregular network (TIN) of image matching points is constructed to get the partitioning local field. Based on the normal distribution of the image matching gross error,a vector descriptor is proposed in the statistics on the local field. Finally,a reasonable threshold is used in eliminating gross errors. The feasibility of the proposed method is verified based on the experiments of two groups of data. The results showed high processing speed and success rate of gross error elimination. This method also provided a new viewpoint to the research of photographic error processing and reliability theory. [full text] [link]
-
, Xiaodong Xiong, Mengqiu Wang, Yihui Lu. (2014) A New Aerial Image Matching Method Using Airborne LiDAR Point Cloud and POS Data. In: Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, Vol.43 No.4: 380-388.
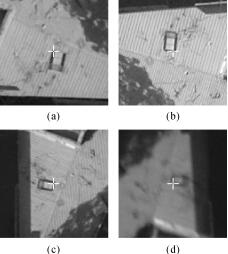
机载激光雷达点云与定位定姿系统数据辅助的航空影像自动匹配方法
Abstract: A novel aerial image tie point matching algorithm with the assistance of airborne LiDAR point cloud and POS data is proposed. Firstly,the conjugate point searching strategy used in traditional correlation coefficient matching is improved and a fast algorithm is presented. Secondly,an automatic camera boresight misalignment calibration method based on virtual ground control points is proposed,then the searching range of image matching is adaptively determined and applied to the image matching of the entire surveying area. Test results verified that the fast correlation coefficient matching algorithm proposed can reduce approximately 25% of the matching time without the loss of matching accuracy. The camera boresight misalignment calibration method can effectively increase the accuracy of exterior orientation elements of images calculated from POS data,and thus can significantly improve the predicted position of conjugate point for tie point matching. Our proposed image matching algorithm can achieve high matching accuracy with multi-scale,multi-view,cross-flight aerial images. [full text] [link]
-
, Bo Wang, Yansong Duan. (2013) An Algorithm of Gross Error Elimination in Image Matching for Large Rotation Angle Images. In: Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, Vol.38 No.10: 1135-1138.
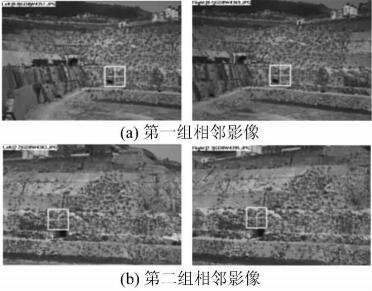
一种针对大倾角影像匹配粗差剔除的算法
Abstract: This paper has proposed an gross error elimination algorithm for image matching based on the imaging surface transformation. Image matching practice which embedded this algorithm in the coarse to fine the matching strategy showes that this algorithm can effective-ly control matching error and correct matching parameters. Experiments with large rotation angle images, such as low-altitude images and close-range images prove that the method can greatly reduce the gross errors in the matching results and ensure the quality and efficiency of image matching. [full text] [link]
-
Jinxin Xiong, , Maoteng Zheng, Yuanxin Ye. (2013) An SRTM Assisted Image Matching Algorithm for Long-strip Satellite Imagery. In: Journal of Remote Sensing, Vol.17 No.5: 1103-1117.
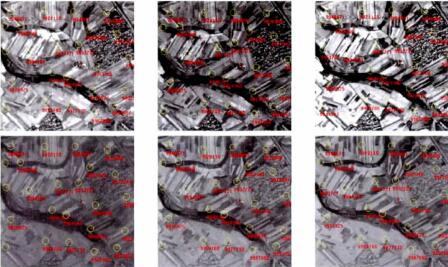
SRTM高程数据辅助的国产卫星长条带影像匹配
Abstract: Faced with the problem of unstable reliability in matching long-strip imagery of Chinese satellite, a matching algorithm is presented using the global Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) data as elevation control. First, this algorithm employs the block partition mechanism, and introduces Local Binary Pattern/Contrast (LBP/C) operator to filter the interest points. Second, the global SRTM data is used to compute the true topographic relief within the image coverage. Based on the true topographic relief, the approximate epipolar line is constructed and the accuracy is analyzed. Third, on the pyramid level, two-dimensional correlation matching is executed to search for the optimal matches along the epipolar line. During the matching process, the geometry rectification method is applied to improve the accuracy of matching. Finally, on the original level, Multi-Photo Geometrically Constrained (MPGC) matching algorithm is adopted to refine the matching result, and Random Sample Consensus (RANSAC) is imbedded to eliminate mismatches. In order to ensure the distribution uniformity of matches, the region-growing algorithm is introduced. The main advantage of the proposed algorithm is that it can realize the automatic matching for long-strip imagery of different Ground Sample Distance (GSD), different visual angles in parallel environment. Through the comparison between the proposed method and the mainly existing methods, the results show that the matching accuracy is improved. [full text] [link]
-
, Maoteng Zheng, Xinyi Wang, Xinhui Huang. (2012) Strip-based Bundle Adjustment of Mapping Satellite-1 Three-line Array Imagery. In: Journal of Remote Sensing, Vol.16 No.6: 84-89.

“天绘一号”卫星三线阵影像条带式区域网平差
Abstract: Space borne linear array sensors have been introduced into photogrammetry since twenty years ago. However, the traditional solution of frame photograph cannot deal with image data obtation by linear array sensors because the position and attitude observations of the spacecraft vary at each scanner line. Thus it is impossible to determinate the exterior orientation parameters of each scanner line. A proper approximation has to be applied to the spacecraft trajectory model to reduce the unknown factors in bundle adjustment. There are three models feasible to represent the satellite trajectory: Quadratic Polynomial Model (QPM), Systematic Error Compensation Model (SECM), and Orientation Image Model (OIM). Revealing the differences of the three sensor models and relationships between different control strategies and the fi nal accuracy of geo-referencing after bundle adjustment is the main purpose of this paper. To fully evaluate the accuracy that the space borne three-line scanner can achieve, experiments with LMP, SECM and OIM triangulation algorithms are performed with a 500 km length data sets of the Mapping Satellite-1 under the WGS-84 coordinate system. [full text] [link]
-
Zuxun Zhang, . (2012) Establishing Geographic Information Infrastructure with Chinese Remote Sensing Imagery. In: Journal of Geomatics, Vol.37 No.5: 7-9.
利用国产卫星影像构建我国地理空间信息
Abstract: Current status of earth observation technology based high resolution satellite is introduced. And the problems in data processing of domestic satellite imagery are discussed. Then key technologies in building the geospatial information of China are proposed. Furthermore, the achievements in fully automatic processing of ZY-3 satellite imagery are presented. [full text] [link]
-
, Xiaodong Xiong. (2012) Automatic Registration of Urban Aerial Imagery with Airborne LiDAR Data. In: Journal of Remote Sensing, Vol.16 No.3: 579-595.
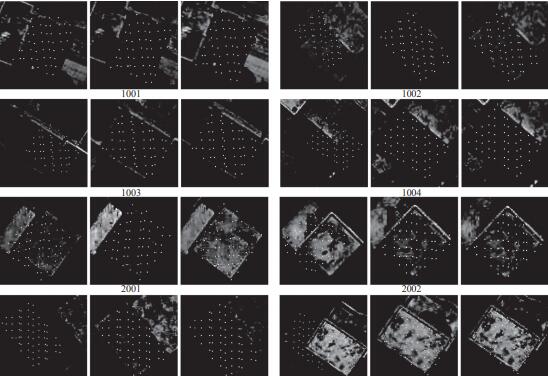
城区机载LiDAR数据与航空影像的自动配准
Abstract: This paper presents a new algorithm for the automatic registration of airborne LiDAR data with aerial images using building corner features as registration primitives. First, three-dimensional building outlines are directly extracted from LiDAR points and building corner features which consist of two orthogonal straight lines are obtained by the regularization of threedimensional building outlines. Straight lines are also extracted from every aerial image. Second, the building corner features are projected onto aerial images and corresponding image corner features are determined using the similarity measures. Lastly, the exterior orientation parameters are refined by bundle adjustment using the corner points of corner features as control points. Iteration strategy is adopted to obtain optimal results. The main advantage of the proposed algorithm is that the three-dimensional building outlines are extracted directly from LiDAR points without transforming LiDAR points into range image or intensity image, and therefore there are no interpolation errors. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can obtain more accurate results in comparison with the registration method based on LiDAR intensity image. [full text] [link]
-
, Lei Wang, Yihui Lu. (2011) Optimization of the Rational Function Model of Satellite Imagery. In: Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, Vol.40 No.6: 756-761.
卫星遥感影像有理函数模型优化方法
Abstract: To solve the problems of over-parameterization and low geo-referencing accuracy of rational function model (RFM), a novel method of parameter optimization based on scatter matrix and elimination transformation and a new method of remnant systematic error compensation without ground control points are proposed. The proposed parameter optimization method can resolve the ill-posed problem of RFM by rejecting all excess parameters. The systematic error compensation method introduces a new correction model with Fourier coefficients. Experimental results indicate that the performance of the proposed method with less parameters is equal to that of the conventional model which all of the 78 parameters. Moreover, the ill-posed problem is effectively eliminated and thus the stabilities of estimated parameters are improved. The systematic error compensation scheme significantly eliminates the remnant systematic error of RFM and improves the geo-referencing accuracy. [full text] [link]
-
, Jinxin Xiong, Xiaodong Xiong, Jiwei Deng. (2011) Main Error Source of Vertical Parallax and Compensation Regression Model of POS Data. In: Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, Vol.40 No.5: 604-609.
POS数据的上下视差误差源检测及误差补偿回归模型
Abstract: Main reason of the existence of systematic error of POS data is analyzed. Error equation of POS-based relative orientation is deduced. Regression model to compensate the systematic error of POS is established. Three sets of aerial images in different scales with POS data are used for experiment. Experimental results show that the systematic error of angular elements in POS data is the main error source which causes large vertical parallax. Compared with original POS data, the POS data corrected by the regression model can significantly decrease vertical parallax. Accuracy of geo-referencing is considerably improved without block adjustment. Satisfying result of experiment verifies the correctness and feasibility of the regression model. [full text] [link]
-
Chang Li, Zuxun Zhang, . (2011) Evaluating the Theoretical Accuracy of Error Distribution of Vanishing Points. In: Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, Vol.40 No.3: 393-396.

灭点误差分布的理论精度评定
Abstract: The related researches of vanishing point have been focusing on its automatic detection and camera calibration for a long time, however there were few researches on its error distribution. Aiming at the closing error issue of lines intersection and the error distribution of vanishing points, we have made in-depth discussions. How to set initial weights for the adjustment solution of single image vanishing points is presented. Furthermore, we propose solving and estimating error distribution of vanishing points based on iteration method with variable weights, co-factor matrix and error ellipse theory. Not only do experimental results reveal the law of error distribution of vanishing points, but also pave the way for the theory and practicability of 3D reconstruction based on vanishing points. [full text] [link]
-
, Binghua Hu, Jianqing Zhang. (2011) Relative Orientation Based on Multiple Conjugate Features. In: Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, Vol.40 No.2: 194-199.
基于多种同名特征的相对定向方法研究
Abstract: To resolve the current problems of relative orientation caused by lacking of obvious feature points in applications of industrial and architectural photogrammetry, a new method of relative orientation based on multiple types of conjugate features is proposed on the basis of the theory of generalized point photogrammetry. The models of independent and continuous relative orientation by conjugate lines and circular curves are addressed respectively. Experimental results show that the proposed approach is feasible in practice, and can get reliable relative orientation results even in the case of a few conjugate points. [full text] [link]
-
, Lei Wu, Liwen Lin, Jiaping Zhao. (2010) Automatic Water Body Extraction Based on LiDAR Data and Aerial Images. In: Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, Vol.35 No.8: 936-940.
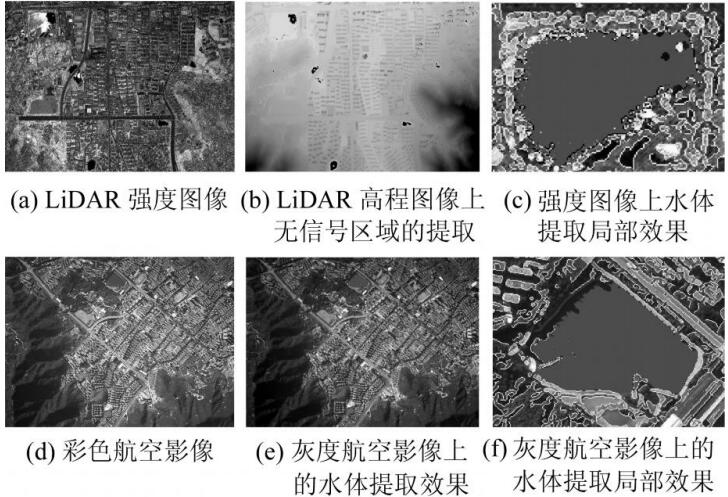
基于LiDAR数据和航空影像的水体自动提取
Abstract: A new approach of automatic water body extraction based on LiDAR data and aerial images is proposed.The LiDAR intensity image and aerial images are co-registrated by SIFT operator.Transformation parameters from LiDAR image to aerial image can be computed by the matched conjugated points.Black regions that have no reflection on height image generated by LiDAR data are automatically extracted.Geometric constraint conditions are used to remove non-water body areas.Edge information is used for region growing with the projected inilial position as initial value.Finally,mathematical morphology techniques are used to get more precise water body areas.Experimental results show that the proposed approach can achieve very good water body information. [full text] [link]
-
, Binghua Hu, Jianqing Zhang. (2011) Absolute Orientation of Large Rotation Angle Images. In: Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, Vol.35 No.4: 427-431.
大旋角影像的绝对定向方法研究
Abstract: Absolute orientation is one of the fundamental issues in Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing. It is also an important topic in computer vision and three-dimensional reconstruction. To overcome the problem of large rotation angles between model coordinates of images and the corresponding world coordinates in close range applications, a new method of absolute orientation which is suitable for large oblique angle image is proposed. Singular value decomposition of rotation matrix is used to obtain accurate initial values of the angular elements. Least squares adjustment with gross error detection is also performed to achieve precise results of absolute orientation. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm is effective and has well potential in various absolute orientation applications. [full text] [link]
-
, Lei Wu, Liwen Lin, Jiaping Zhao. (2010) Condition Numbers for Evaluation of Ill-Posed Problems in Photogrammetry. In: Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, Vol.35 No.3: 308-312.
摄影测量中病态问题的条件数指标分析
Abstract: We discuss the principle of condition numbers that used for evaluating the extent of ill-posed problem of normal matrix.There is a contradiction between the stability of solution and the condition number of resection in photogrammetry.We find that it is not suitable in all cases to evaluate the extent of ill-posed problem by condition numbers.Three types of possible risks for evaluation of ill-condition extent with condition numbers were addressed in detail.Removing of outliers and re-parameterization are the prerequisites for evaluation of ill-condition extent with condition numbers.There are two effects of re-parameterization for ill-posed problems.One is improving the problem of ill-condition caused by numerical computation,and the other is avoiding the risk of using norm to evaluate the extent of ill-condition.Results of simulated experiments show that the proposed approach is validate for improving the problem of ill-condition. [full text] [link]
-
, Jiwei Deng, Jinxin Xiong, Hongya Zhang. (2010) Aerial Photographic Route Optimization Based on DEM and Simulated Bundle Adjustment. In: Journal of Geomatics, Vol.35 No.5: 30-32.
基于DEM及模拟平差的航空摄影航线优化设计方法
Abstract: 采用了模拟数据解算及变基线敷设航线的方法,自动解算了地形、相机参数及飞行器参数最优重叠度,设计出最适合该测区的航线。... [full text]
-
, Wei Kong. (2009)
Pose Determination of Space Object with Single Image. In: Journal of Xi'an Jiaotong University, 43(9): 56-61.
利用单幅影像的空间目标姿态测定方法
Abstract: A new method for space object pose determination by single image with known exterior orientation parameters is proposed. Initial values of object pose under world coordinate system are acquired by space resection and coordinate transformation. Then , precise pose parameters are obtained by least squares adjustment wit h collinearity equations where t he exterior orientation pa2 rameters are known. The proposed approach avoids t he synchronization problem of determining object pose wit h two or more cameras. Bot h simulated and real data experiments verify t he cor2 rect ness and validity of t he proposed approach. The experimental results show t hat t he precision of pose determination is significantly influenced by focal length of camera and distance between object and camera , t hus the number of control points and focal lengt h ought to be f ully considered according to the precision requisition for application. [full text]
-
, Yazhou Ding. (2009) Approximate Epipolar Image Generation of Linear Array Satellite Stereos with Rational Polynomial Coefficients. In: Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 34(9): 1068-1071.

基于有理多项式系数的线阵卫星近似核线影像的生成
Abstract: The basic principle of projective locus method to calculate local approximate epipolar image of linear array satellite stereo is discussed.A Line segment fitting approach is proposed to improve the precision of epipolar image.A new object space longitude and latitude based approximate epipolar image re-sampling approach is put forward.The proposed approach has well potential in dense image matching for generating high precision digital elevation models.Both searching range and mismatch possibility can be decreased.The experimental results show that the projective locus method is qualified for calculating local epipolar lines.The precision of line segment fitting is superior to that of traditional line fitting method.There is no y-parallax on re-sampled epipolar image with the proposed approach,which is advantageous for dense image matching.The precision of reverse calculation from epipolar image coordinates to original image coordinates is better than 0.04 pixel,which verifies the correctness of the proposed re-sampling approach. [full text] [link]
-
. (2009) Geometric Processing of Low Altitude Remote Sensing Images Captured by Unmanned Airship. In: Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, Vol.34 No.3: 284-288.

无人驾驶飞艇低空遥感影像的几何处理
Abstract: The composition and technical characteristics of low altitude remote sensing system based on unmanned airship are introduced. The unmanned airship automated flies along the predefined routes and captures image sequences under the controlment of autopilot system. Geometric processing of captured low altitude stereo images, such as image matching, relative orientation, bundle block adjustment, panorama and orthoimage generation, are addressed in detail. Experimental results show that the developed system is qualified for high overlap and high resolution stereo imagery acquisition, and has good potential in large scale mapping and precise three dimensional reconstruction areas. [full text] [link]
-
. (2008) Reconstruction of Circles and round rectangles by generalized point photogrammetry. In: Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology. Vol.40 No.1: 136-140.
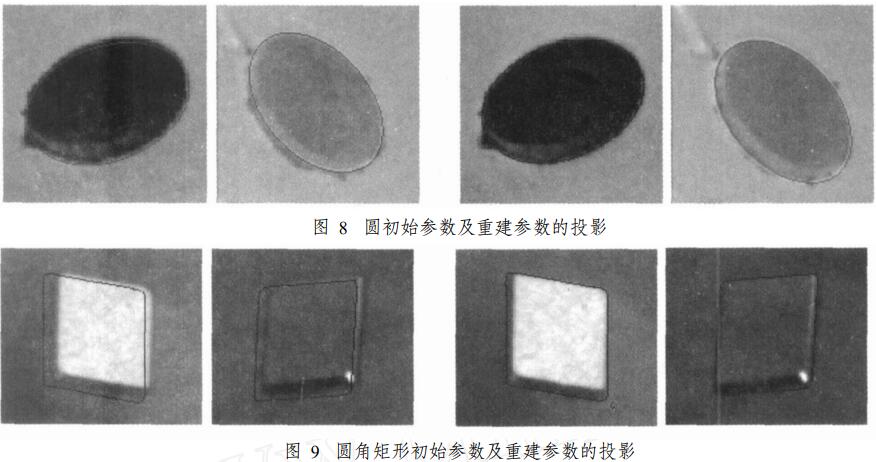
基于广义点摄影测量的圆和圆角矩形三维重建
Abstract: The composition and technical characteristics of low altitude remote sensing system based on unmanned airship are introduced. The unmanned airship automated flies along the predefined routes and captures image sequences under the controlment of autopilot system. Geometric processing of captured low altitude stereo images, such as image matching, relative orientation, bundle block adjustment, panorama and orthoimage generation, are addressed in detail. Experimental results show that the developed system is qualified for high overlap and high resolution stereo imagery acquisition, and has good potential in large scale mapping and precise three dimensional reconstruction areas. [full text]
-
Youchuan Wan, Liangming Liu, . (2007) Development of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing in China. In: Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, No.1: 1-4.
我国摄影测量与遥感发展探讨
Abstract: 随着摄影测量发展到数字摄影测量阶段及多传感器、多分辨率、多光谱、多时段遥感与其他边缘学科的交叉渗透、相互融合,摄影测量与遥感已逐渐发展成为一门新型的地球空间信息科学。分析近年来我国摄影测量与遥感技术表现出的许多新的特点,分别从数字摄影测量、航空摄影自动定位技术、近景摄影测量、低空摄影测量、机载激光扫描、稀少或无地面控制的卫星影像测图及应用、SAR数据处理、多源空间数据挖掘、遥感图像处理的智能化实用系统等方面予以总结。 [full text]
-
, Yong Zhang. (2006) Direct Geo-referencing of SPOT 5 HRS Imagery Without (or with a Few) Ground Control Point. In: Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, Vol.31 No.11: 941-944.
SPOT 5 HRS立体影像无(稀少)控制绝对定位技术研究
Abstract: The photographic principle of SPOT 5 HRS is discussed in detail.By a series of coordinate system transforming,the rigorous orbit model of direct geo-referencing without ground control point is established.Experimental results of three datasets show that there are systematic errors existed.Once a ground control point is introduced,the result is improved tremendously.Results of 580 km test dataset with one ground control point are still better than 20 m for the planar position and about 10m for the altitude.It shows that the orbit itself is very stable.The HRS imagery has promising potential for various applications. [full text] [link]
-
. (2005) Automatic Extraction of Tree Rows and Hedges by Data Integration. In: Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, Vol.30 No.11: 970-974.

基于数据融合的行树与篱笆三维信息自动提取
Abstract: This paper mainly focuses on the integration of GIS data, DSM information and CIR stereo imagery to derive automatically tree rows and hedges in the open landscape. Different approaches, such as segmentation by CIE L*a*b, edge extraction, linking and grouping, and verifying with 3D information, are successfully integrated to extract the objects of interest. The extracted tree rows and hedges can be used to update the GIS database, to derive wind erosion risk fields for soil monitoring and preservation. [full text] [link]
-
, Yong Zhang. (2005) Analysis of Precision of Relative Orientation and Forward Intersection with High-overlap Images. In: Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, Vol.30 No.2: 126-130.
大重叠度影像的相对定向与前方交会精度分析
Abstract: Image sequence acquired by digital cameras has the advantages of high-overlap and redundancy of observations, which makes it more and more popular in 3D reconstruction. Precision of relative orientation and forward intersection with high overlapping image sequence is analyzed. The higher the overlap is, the better the result of relative orientation is. The more images are used, and the bigger the intersection angle is, the higher the precision of forward intersection is. In practice, images with 80 % overlap are optimal for 3D reconstruction and other applications. [full text] [link]
-
, Zuxun Zhang, Jianqing Zhang. (2004) Three-Dimensional Reconstruction and Visual Inspection of Industrial Sheetmetal Parts with Image Sequence. In: Tsinghua Science and Technology, Vol. 44, No.4: 534-537.
基于序列图像的工业钣金件三维重建与视觉检测
Abstract: 针对目前工业制造领域面临的难题,提出利用非量测数字摄像机进行工业钣金件高精度三维重建与视觉检测。采用二维直接线性变换分解摄像机参数初值并结合光束法平... [full text]
-
, Jingnan Liu, Zuxun Zhang, Jianqing Zhang. (2004) Imprecision Inspection of Sheetmetal Parts with Non-metric CCD Camera. In: Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, Vol. 33, No.2: 132-137.
基于非量测CCD摄像机的钣金件误差检测
Abstract: A new approach of three2dimensional reconstruction and inspection of industrial sheetmetal parts with non2metric CCD camera is proposed. Principle of line segment least squares template matching to extract precise points and lines from imagery is discussed. Wire2frame model of the sheetmetal part can be accurately reconstructed with hybrid point2line photogrammetry. One2dimensional template matching and direct object space solution is used to reconstruct complex shapes such as circles and connected arcs and lines. Producing imprecision can be inspected automatically or interactively by the results of reconstruction. The proposed inspection technique has the advantages of low cost of hardware and can run automatically and fastly. Inspection results of several parts are very satisfying. [full text]
-
, Cheng Wang, Zuxun Zhang, Jianqing Zhang. (2004) Object Space-based Matching and Reconstruction of Circles. In: Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, Vol. 40, No.2: 92-95.
基于物方直接解的圆匹配与重建
Abstract: 提出一种基于物方直接解的圆匹配与重建方法,建立了灰度影像与空间圆参数间的函数关系,根据已知的相片内外方位元素及空间圆参数的初值,利用直线段最小二乘模板匹配方法直接获取空间圆的参数。系统论述了基于物方直接解和直线段最小二乘模板匹配方法进行空间圆匹配与重建的数学模型。实际图像数据的试验结果表明,本算法具有较高的重建精度。 [full text] [link]
-
, Jianqing Zhang. (2003) Orientation of Remote Sensing Image Pairs from Different Orbits. In: Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, Vol.28 No.5: 521-524.
异轨遥感立体像对外方位元素的求解算法
Abstract: This paper mainly focuses on the approach of obtaining camera orientation parameters of remote sensing image pairs from different orbits.The fundamental mathematical models of obtaining camera orientation parameters from collinearity equations and coplanar conditions are discussed in detail.To combine the two models,spatial resection model based on coplanar conditions is modified.Results of the combined model can be obtained with adjustment by observation equations.Algorithms of how to calculate the initial values of orientation parameters are also addressed.The proposed approach is tested with a stereo image pair and some results are given. [full text] [link]
-
, Zuxun Zhang, Jianqing Zhang. (2003) Dimensional Inspection of Industrial Parts with Image Sequence. In: Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University, Vol.37 No.9: 1447-1451.
基于序列图像的工业零件尺寸检测技术
Abstract: 提出利用像面上的点、直线信息进行混合光束法平差,对工业零件进行高精度三维重建并检测其尺 寸误差.介绍了零件坐标系与物方坐标系之间的变换方法,讨论了直线摄影测量误差方程式的基本形式、基于距离的改化形式以及点线混合光束法平差的数学模型, 提出在适当选取直线观测值的权值时,可以按间接平差模型解算直线空间前方交会.所开发的工业零件视觉检测系统可全自动运行,取得了约0.1 mm的实验精度,为工业领域中广泛存在的以直线段为主要特征的工业零件如钣金件的自动化三维检测提供了一条有效途径. [full text]
-
, Zuxun Zhang. (2003) Camera Calibration using 2D-DLT and Bundle Adjustment. In: Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, Vol.27 No.6: 566-571.
利用二维DLT及光束法平差进行数字摄像机标定
Abstract: A flexible camera calibration technique using 2D-DLT and bundle adjustment with planar scenes is proposed in this paper. The equation of principal vertical line under image coordinate system represented by 2D-DLT parameters is worked out using the correspondence between collinearity equations and 2D-DLT. Proof of ambiguities in camera parameter decomposition with 2D-DLT parameters is given. Initial value of principal point can be obtained with at least two equations of principal vertical lines. Proof of critical motion sequences(CMS) is also given in detail. The practical decomposition algorithm of extrinsic parameters using initial values of principal point, focal length and 2D-DLT parameters is discussed elaborately. Planar-scene camera calibration algorithm with bundle adjustment(using collinearity equations) is addressed. For the proposed technique, either the camera or the planar pattern can be moved freely, and the motion need not be known. Very good results have been obtained with both computer simulations and real data calibration. [full text] [link]
-
, Shaoquan Xu, Zemin Wang. (2001) Ambiguity Resolution Approach in Combined GPS/GLONASS Positioning. In: Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, Vol.26 No.1: 58-63.
GPS/GLONASS组合定位中模糊度的处理
Abstract: A flexible camera calibration technique using 2D-DLT and bundle adjustment with planar scenes is proposed in this paper. The equation of principal vertical line under image coordinate system represented by 2D-DLT parameters is worked out using the correspondence between collinearity equations and 2D-DLT. Proof of ambiguities in camera parameter decomposition with 2D-DLT parameters is given. Initial value of principal point can be obtained with at least two equations of principal vertical lines. Proof of critical motion sequences(CMS) is also given in detail. The practical decomposition algorithm of extrinsic parameters using initial values of principal point, focal length and 2D-DLT parameters is discussed elaborately. Planar-scene camera calibration algorithm with bundle adjustment(using collinearity equations) is addressed. For the proposed technique, either the camera or the planar pattern can be moved freely, and the motion need not be known. Very good results have been obtained with both computer simulations and real data calibration. [full text] [link]
-
Yingbing Li, Shaoquan Xu, . (2001) The Application of Spectrum Analysis in GPS Auto-monitoring System. In: Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, Vol.26 No.4: 343-348.
谱分析在GPS自动化监测系统中的应用研究
Abstract: Deformation monitoring system is the safeguard of dam.Space estate and time characteristic of dam are attained by deformation monitoring,which is used to investigate the stability,discover the problems,take some measures,study deformation mechanism,validate designing theory as well as set up proper prediction model and methods of the dam.The real-time effective data processing and analysis are important in dam deformation monitoring.Dynamic deformation is taken as placidity random course.Dam deformation as well as water level change of reservoir and temperature variation is taken as linear system in this paper.Fast Fourier Transform transfers those signals from time domain to frequency domain. The deformation data,including water level of reservoir,are taken from the database of Geheyan GPS auto-monitoring system from June 10,1998 to October 23,1999,in total 491 days.Temperature data only about 343 days which are between June 10,1998 and May 18,1999.Those data are prepared as 4 data each day by tri-spline function.A difference filter is used to remove long-term trend.The Power spectrum of dam deformation,water level and temperature are shown in Fig.5,Fig.6 and Fig.7.From the figures we know their main frequency are near 1 Hz(about 1 day).Day change of water level of reservoir and temperature is one of main reasons of day deformation of dam.Delivering function curve of deformation and water level is shown in Fig.8.Delivering function curve of deformation and temperature is shown in Fig.9.The signals energies both reach max value at 1.884 Hz.Power spectrum of velocity of dam deformation,water level of reservoir and temperature are shown in Fig.10,Fig.11 and Fig.12. A discussion is carried out at the end of this paper.In order to verify the performance of the result derived from spectrum analysis,cross correlation between deformation and water level as well as temperature is studied,and the result is presented in Fig.13 and Fig.14.However,there is only one temperature data available,but four temperature data are required for analysis.From the discussion we knew that it is a big problem in such a condition.At last two conclusions are drawn:1) Day change of water level of reservoir and temperature is one of main reason of day deformation of dam.If there were only two reasons,the effect of water level is about 63% and temperature is about 37%.2) Power spectrum of velocity of dam deformation,water level of reservoir and temperature shown very similar and their energy is mostly in high frequency. The velocity of water level of reservoir and temperature is one of the reasons of velocity of dam deformation.But there are still some further work to do in future.Long-term data and more data for each day should be studied further if possible. [full text] [link]
-
Yingbing Li, Shaoquan Xu, , Xiaohong Zhang. (2001) Spectral Analysis in Application of Automatic GPS based Dam Deformation Monitoring. In: Global Positioning System, Vol.26 No.1: 31-34.
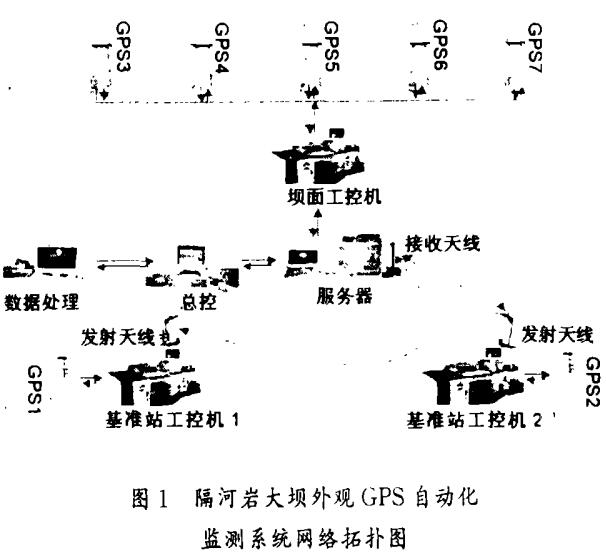
谱分析在大坝外观GPS自动化监测中应用的研究
Abstract: Deformation monitoring system is the safeguard of dam.Space estate and time characteristic of dam are attained by deformation monitoring,which is used to investigate the stability,discover the problems,take some measures,study deformation mechanism,validate designing theory as well as set up proper prediction model and methods of the dam.The real-time effective data processing and analysis are important in dam deformation monitoring.Dynamic deformation is taken as placidity random course.Dam deformation as well as water level change of reservoir and temperature variation is taken as linear system in this paper.Fast Fourier Transform transfers those signals from time domain to frequency domain. The deformation data,including water level of reservoir,are taken from the database of Geheyan GPS auto-monitoring system from June 10,1998 to October 23,1999,in total 491 days.Temperature data only about 343 days which are between June 10,1998 and May 18,1999.Those data are prepared as 4 data each day by tri-spline function.A difference filter is used to remove long-term trend.The Power spectrum of dam deformation,water level and temperature are shown in Fig.5,Fig.6 and Fig.7.From the figures we know their main frequency are near 1 Hz(about 1 day).Day change of water level of reservoir and temperature is one of main reasons of day deformation of dam.Delivering function curve of deformation and water level is shown in Fig.8.Delivering function curve of deformation and temperature is shown in Fig.9.The signals energies both reach max value at 1.884 Hz.Power spectrum of velocity of dam deformation,water level of reservoir and temperature are shown in Fig.10,Fig.11 and Fig.12. A discussion is carried out at the end of this paper.In order to verify the performance of the result derived from spectrum analysis,cross correlation between deformation and water level as well as temperature is studied,and the result is presented in Fig.13 and Fig.14.However,there is only one temperature data available,but four temperature data are required for analysis.From the discussion we knew that it is a big problem in such a condition.At last two conclusions are drawn:1) Day change of water level of reservoir and temperature is one of main reason of day deformation of dam.If there were only two reasons,the effect of water level is about 63% and temperature is about 37%.2) Power spectrum of velocity of dam deformation,water level of reservoir and temperature shown very similar and their energy is mostly in high frequency. The velocity of water level of reservoir and temperature is one of the reasons of velocity of dam deformation.But there are still some further work to do in future.Long-term data and more data for each day should be studied further if possible. [full text]
-
Xiaohong Zhang, Zhenghang Li, . (2000) Effective Strategies to Improve the Precision of GPS Positioning in Mountain Areas. In: Dynamic Geodesy, Vol.16, No.2/3: 56-60.
-
, Shaoquan Xu. (2000) Research on GLONASS Broadcast Ephemeris Orbit Computation. In: GPS World of China, Vol.25, No.1: 58-62.
GLONASS广播历书轨道计算方法研究
Abstract: GLONASS与GPS观测数据联合处理引起了许多GPS用户的广泛关注。本文在简单介绍GLONASS系统的基础上,阐述了常用的广播历书轨道积分模型,并提出了一种新的积分方法。该方法具有编程简单,运算速度快等优点。 [full text]
-
Shaoquan Xu, . (2000) Precision Analysis of Combined GPS/GLONASS Positioning System. In: WTUSM Bulletin of Science and Technology, No.1: 22-25.
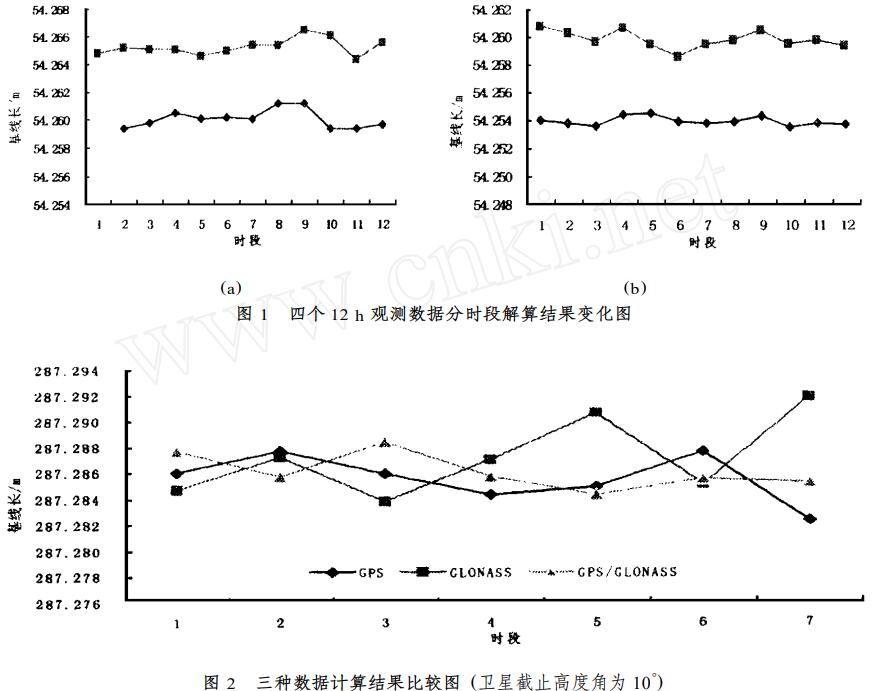
GPS/GLONASS组合定位系统的精度
Abstract: 介绍了GLONASS的组成及其运行状况,并与GPS进行了比较.为了检验GPS/GLONASS组合定位系统的灵敏度及其定位精度,在进行大量实验的基础上,对GPS、GLONASS、GPS/GLONASS三... [full text]
-
, Zemin Wang. (1999) Baseline Resolution Approach of GPS Data and Compatibility Check of Control Points. In: TianLu HangCe.
GPS的基线解算及已知点兼容性检验
Abstract: 全球定位系统(简称GPS)是美国国防部为满足军事部门对海上、陆地和空中设施进行高精度导航和定位要求而建立的,它具有全球性、全天候、连续的精密三维导航与定位能力。经过全世界科技工作者、仪器生产厂商的共同努力,GPS定位技术日趋成熟,而且具有自动化... [full text]
-
, Zemin Wang, Shaoquan Xu, Yingbing Li. (1999) Development of Multimedia Teaching Software "GPS Receivers and Applications". In: TianLu HangCe, No.4: 30-32.
多媒体教学软件“GPS仪器及软件使用”的研制
Abstract: 本文简述了“GPS仪器及软件使用”多媒体教学软件的设计思想和制作过程。该软件利用近几年才出现并迅速发展的计算机多媒体技术,图文并茂、直观形象地演示了GPS测量仪器... [full text]
-
, Shaoquan Xu, Yingbing Li. (1999) Research on the Applications of GPS/GLONASS Integrated Positioning System. In: Journal of Xi’an Research Institute of Surveying and Mapping, Vol.19, No.4: 22-27.
- All
- All
- English Conference
- Chinese Conference
-
Kun Huang, , Rongjun Qin, Xu Huang. (2018) Block adjustment method for optical satellite on-orbit geometric calibration. In: ASPRS Annual Conference 2018At: Denver, Colorado.
Abstract: On-orbit geometric calibration is a key technology to guarantee the interior geometric quality and direct positioning accuracy of high-resolution optical satellite images, in which block adjustment are used to solve the precise value of interior and exterior calibration parameters. In order to improve the accuracy, efficiency and robustness of geometric calibration of multi-chip TDICCD triangular mechanical staggered stitching optical sensor, this paper proposed an improved Conjugate Gradient Bundle Adjustment (CGBA) method. Taking the high-resolution optical camera of Chinese Mapping Satellite-1 for example, the design of TDICCD triangular mechanical staggered stitching is illustrated. The strict imaging geometric calibration model is constructed and optimized. Then, the CGBA method is deduced by calculus of variations. A preconditioning method based on improved incomplete Cholesky factorization is adopt to reduce the condition number of coefficient matrix, as well as to accelerate the iteration rate of CGBA. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed geometric calibration method can effective improve the interior and exterior geometric quality of images, the improved CGBA can effectively conquer the ill-conditioned problem and improve the calculation efficiency while maintaining actual accuracy.
-
Xinyi Liu, , Qian Li. (2018) Automatic Pedestrian Crossing Detection and Impairment Analysis Based on Mobile Mapping System. In: ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 4, p.251.
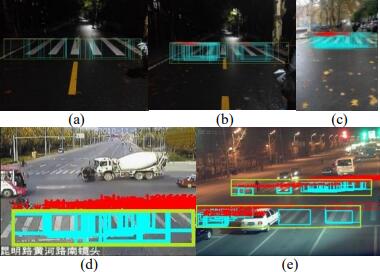
Abstract: Pedestrian crossing, as an important part of transportation infrastructures, serves to secure pedestrians’ lives and possessions and keep traffic flow in order. As a prominent feature in the street scene, detection of pedestrian crossing contributes to 3D road marking reconstruction and diminishing the adverse impact of outliers in 3D street scene reconstruction. Since pedestrian crossing is subject to wearing and tearing from heavy traffic flow, it is of great imperative to monitor its status quo. On this account, an approach of automatic pedestrian crossing detection using images from vehicle-based Mobile Mapping System is put forward and its defilement and impairment are analyzed in this paper. Firstly, pedestrian crossing classifier is trained with low recall rate. Then initial detections are refined by utilizing projection filtering, contour information analysis, and monocular vision. Finally, a pedestrian crossing detection and analysis system with high recall rate, precision and robustness will be achieved. This system works for pedestrian crossing detection under different situations and light conditions. It can recognize defiled and impaired crossings automatically in the meanwhile, which facilitates monitoring and maintenance of traffic facilities, so as to reduce potential traffic safety problems and secure lives and property. [full text] [link]
-
Xu Huang, , Zhaoxi Yue. (2016) Image-guided Non-local Dense Matching with Three-steps Optimization. (Oral Presentation). In: International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, July 12-19, Prague, Czech Republic, Volume III-3:67-74.
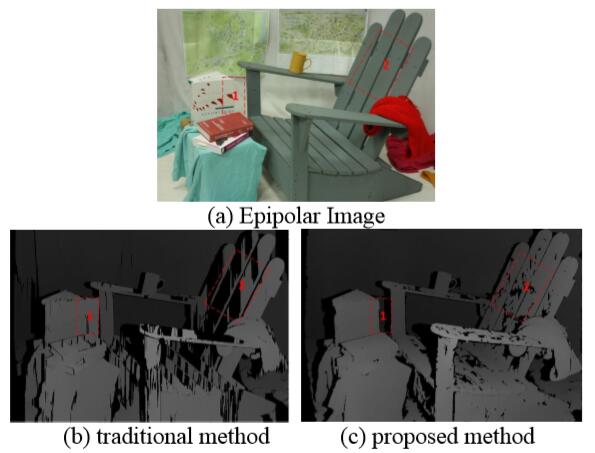
Abstract: This paper introduces a new image-guided non-local dense matching algorithm that focuses on how to solve the following problems: 1) mitigating the influence of vertical parallax to the cost computation in stereo pairs; 2) guaranteeing the performance of dense matching in homogeneous intensity regions with significant disparity changes; 3) limiting the inaccurate cost propagated from depth discontinuity regions; 4) guaranteeing that the path between two pixels in the same region is connected; and 5) defining the cost propagation function between the reliable pixel and the unreliable pixel during disparity interpolation. This paper combines the Census histogram and an improved histogram of oriented gradient (HOG) feature together as the cost metrics, which are then aggregated based on a new iterative non-local matching method and the semi-global matching method. Finally, new rules of cost propagation between the valid pixels and the invalid pixels are defined to improve the disparity interpolation results. The results of our experiments using the benchmarks and the Toronto aerial images from the International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing (ISPRS) show that the proposed new method can outperform most of the current state-of-the-art stereo dense matching methods. [full text]
-
Yanfeng Zhang, , Yi Zhang, Xin Li. (2016) Automatic Extraction of DTM from Low Resolution DSM by Two-steps Semi-global Filtering (Oral Presentation). In:International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, July 12-19, Prague, Czech Republic, Volume III-3:249-255.
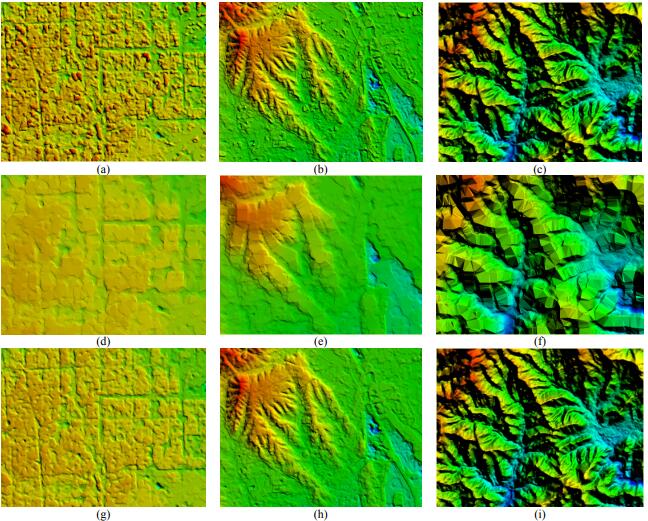
Abstract: Automatically extracting DTM from DSM or LiDAR data by distinguishing non-ground points from ground points is an important issue. Many algorithms for this issue are developed, however, most of them are targeted at processing dense LiDAR data, and lack the ability of getting DTM from low resolution DSM. This is caused by the decrease of distinction on elevation variation between steep terrains and surface objects. In this paper, a method called two-steps semi-global filtering (TSGF) is proposed to extract DTM from low resolution DSM. Firstly, the DSM slope map is calculated and smoothed by SGF (semi-global filtering), which is then binarized and used as the mask of flat terrains. Secondly, the DSM is segmented with the restriction of the flat terrains mask. Lastly, each segment is filtered with semi-global algorithm in order to remove non-ground points, which will produce the final DTM. The first SGF is based on global distribution characteristic of large slope, which distinguishes steep terrains and flat terrains. The second SGF is used to filter non-ground points on DSM within flat terrain segments. Therefore, by two steps SGF non-ground points are removed robustly, while shape of steep terrains is kept. Experiments on DSM generated by ZY3 imagery with resolution of 10-30m demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method. [full text]
-
Daifeng Peng, . (2016) Building Change Detection by Combining LiDAR Data and Ortho Image. (Poster). In:International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, July 12-19, Prague, Czech Republic, Volume XLI-B3:669-676.
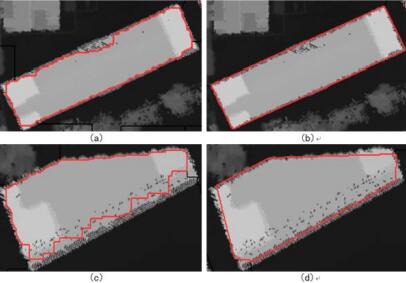
Abstract: The elevation information is not considered in the traditional building change detection methods. This paper presents an algorithm of combining LiDAR data and ortho image for 3D building change detection. The advantages of the proposed approach lie in the fusion of the height and spectral information by thematic segmentation. Furthermore, the proposed method also combines the advantages of pixel-level and object-level change detection by image differencing and object analysis. Firstly, two periods of LiDAR data are filtered and interpolated to generate their corresponding DSMs. Secondly, a binary image of the changed areas is generated by means of differencing and filtering the two DSMs, and then thematic layer is generated and projected onto the DSMs and DOMs. Thirdly, geometric and spectral features of the changed area are calculated, which is followed by decision tree classification for the purpose of extracting the changed building areas. Finally, the statistics of the elevation and area change information as well as the change type of the changed buildings are done for building change analysis. Experimental results show that the completeness and correctness of building change detection are close to 81.8% and 85.7% respectively when the building area is larger than 80 2 m , which are increased about 10% when compared with using ortho image alone. [full text]
-
, Yi Wan, Bo Wang, Yifei Kang, Jinxin Xiong. (2015) Automatic Processing of Chinese GF-1 Wide Field of View Images. In: 36th International Symposium on Remote Sensing of Environment, May 11-15, Berlin, Germany, Volume XL-7/W3: 729-734.

Abstract: The wide field of view (WFV) imaging instrument carried on the Chinese GF-1 satellite includes four cameras. Each camera has 200km swath-width that can acquire earth image at the same time and the observation can be repeated within only 4 days. This enables the applications of remote sensing imagery to advance from non-scheduled land-observation to periodically land-monitoring in the areas that use the images in such resolutions. This paper introduces an automatic data analysing and processing technique for the wide-swath images acquired by GF-1 satellite. Firstly, the images are validated by a self-adaptive Gaussian mixture model based cloud detection method to confirm whether they are qualified and suitable to be involved into the automatic processing workflow. Then the ground control points (GCPs) are quickly and automatically matched from the public geo-information products such as the rectified panchromatic images of Landsat-8. Before the geometric correction, the cloud detection results are also used to eliminate the invalid GCPs distributed in the cloud covered areas, which obviously reduces the ratio of blunders of GCPs. The geometric correction module not only rectifies the rational function models (RFMs), but also provides the self-calibration model and parameters for the non-linear distortion, and it is iteratively processed to detect blunders. The maximum geometric distortion in WFV image decreases from about 10-15 pixels to 1-2 pixels when compensated by self-calibration model. The processing experiments involve hundreds of WFV images of GF-1 satellite acquired from June to September 2013, which covers the whole mainland of China. All the processing work can be finished by one operator within 2 days on a desktop computer made up by a second-generation Intel Core-i7 CPU and a 4-solid-State-Disk array. The digital ortho maps (DOM) are automatically generated with 3 arc second Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM). The geometric accuracies of the generated DOM are 20m for camera-2 and 3, and 30m accuracy for camera-1 and 4. These products are now widely used in the fields of land and resource investigation, environment protection, and agricultural research. [full text]
-
, Xiaodong Xiong, Xiangyun Hu. (2013) Rigorous LiDAR Strip Adjustment with Triangulated Aerial Imagery. In: ISPRS, Laser Scanning 2013, Nov. 11-13, Antalya, Turkey, Volume II-5/W2: 361-366.
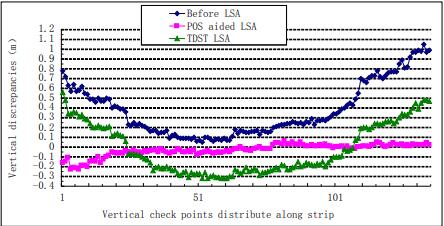
Abstract: This paper proposes a POS aided LiDAR strip adjustment method. Firstly, aero-triangulation of the simultaneously obtained aerial images is conducted with a few photogrammetry-specific ground control points. Secondly, LiDAR intensity images are generated from the reflectance signals of laser foot points, and conjugate points are automatically matched between the LiDAR intensity image and the aero-triangulated aerial image. Control points used in LiDAR strip adjustment are derived from these conjugate points. Finally, LiDAR strip adjustment of real data is conducted with the POS aided LiDAR strip adjustment method proposed in this paper, and comparison experiment using three-dimensional similarity transformation method is also performed. The results indicate that the POS aided LiDAR strip adjustment method can significantly correct the planimetric and vertical errors of LiDAR strips. The planimetric correction accuracy is higher than average point distance while the vertical correction accuracy is comparable to that of the result of aero-triangulation. Moreover, the proposed method is obliviously superior to the traditional three-dimensional similarity transformation method. [full text]
-
Jinxin Xiong, . (2012) Combined Multi-View Matching Algorithm with Multiple Long-Strip Satellite Imagery from Different Orbits. In: ISPRS 2012 Congress, September 2012, Melbourne, Australia. ISPRS, 38(B3): 87-92.
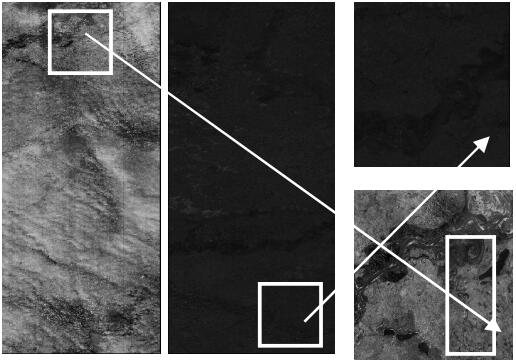
Abstract: Existing matching algorithms aim to match conjugate points among overlapping satellite scenes acquired from the same orbit and can generally achieve good matching performance. Unfortunately, no algorithm can avoid the difficulty of simultaneously processing the data sets of long-strip imagery acquired from different orbits. In this paper, the combined matching algorithm we propose introduces the LBP/C operator, which, when combined with existing feature detectors for the first time, can make possible the extraction of more stable interest points and candidates. At the same time, based on the typical characteristics of Chinese satellite imagery, we improved the filter method and achieved an effective combination of several image matching algorithms. A comparison among several kinds of matching transfer modes was presented; and to evaluate this algorithm, Chinese Mapping Satellite-I data are used as the reference data. [full text]
-
, Maoteng Zheng. (2012) Bundle Block Adjustment with Self-Calibration of Long Orbit CBERS-02B Imagery. In: ISPRS 2012 Congress, August 2012, Melbourne, Australia. ISPRS, 38(B1): 291-296.

Abstract: CBERS-02B was the first high resolution earth observation satellite in China, which adopted linear array push-broom sensor. The nadir ground resolution of the on board HR camera was 2.36 m. However, the accuracies of the on-board GPS receiver and star tracker were very limited due to the technical restrictions. The accuracy of direct geo-referencing by the on-board measurements of position and attitude parameters was about 1 kilometre, which restrained the wide applications of the CBERS-02B imagery in the surveying and mapping field. It is necessary to perform the bundle block adjustment to improve the accuracy of geo-referencing. A proper sensor model has to be adopted during the bundle block adjustment using strict physical sensor model with long orbit data, in order to solve the problem of too many unknown exterior orientation parameters (EOPs). Several sensor models have been discussed, such as quadratic polynomial model, systematic error compensation model, orientation image model, and piecewise polynomial model. The combination of the systematic error compensation model and the orientation image model will be used to deal with the CBERS-02B imagery in this paper. Furthermore, three TDI-CCD linear arrays were fixed on the focal plane of the HR camera. The middle CCD array was shifted against the left and the right one. The level 1A image used in this paper was mosaicked by the three sub-images collected by the left, the middle and the right CCD, respectively. But there were some displacements among the three sub-images in the mosaicked image and the three CCD arrays may not be rigorously parallel. The angular parameter a and the translation parameters x, y of each CCD refer to the theoretical position on the focal plane is used to model the interior distortions, so there are totally 9 interior distortion parameters, although some of them are not significant. The laboratory calibrated parameters of the image sensor are usually different from the true values after launch. So a self-calibration strategy should be applied in the bundle block adjustment. Plenty of automatically matched GCPs with precision of 10 meters in plane and 20 meters in height are used to perform the bundle adjustment. Both the systematic error compensation model and the orientation image model with the interior selfcalibration parameters are used in the bundle block adjustment to eliminate the systematic errors caused by the camera internal distortions and to improve the precision of geo-referencing. A best combination of interior orientation parameters (IOPs) is drawn from the adjustment results with different combinations of these IOPs. Besides, there may be some gross errors in the automatically matched GCPs. The gross errors among GCPs may lead to unusual variation of the exterior orientation elements by time. Methods of enlarging the intervals of orientation image and increasing the weights of the position and attitude observations are applied in the combined bundle block adjustment to remove the influence of gross errors of GCPs. The preliminary experimental results show that for longer than 1000 km orbit data, the average accuracy of self-calibrated bundle block adjustment combined with GPS and star tracker observations is 2 pixels better than that without self-calibration. The planar position accuracies in X and Y of check points are 8 m and 7 m respectively. [full text]
-
, Maoteng Zheng, Tao Ke. (2011) Triangulation of Spaceborne Three-Line Array Imagery with Different Sensor Models. In: ASPRS 2011 Annual Conference, May 2011, Milwaukee, USA.
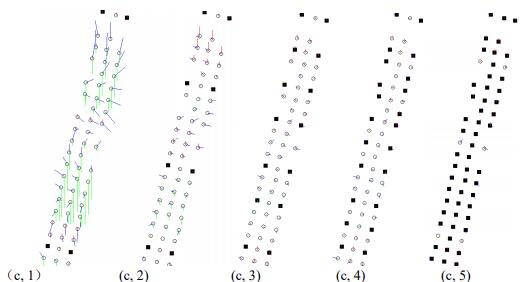
Abstract: Spaceborne linear array sensors have been introduced into photogrammetry since more than twenty years ago. The traditional solution of frame photograph cannot deal with image data of linear array sensor anymore, because the position and attitude of the spacecraft vary at each scanner line. Thus the number of unknowns would be extremely large and it is impossible to determinate the exterior orientation parameters of each scanner line. A proper approximation has to be applied to model the spacecraft trajectory to reduce the unknowns in triangulation. There are three models feasible to represent the satellite trajectory: Quadratic Polynomial Model (QPM), Systematic Error Compensation Model (SECM), and Orientation Image Model (OIM). Revealing the differences of the three sensor models and relationships between different control strategies and the final accuracy of georeferencing after bundle adjustment is the main purpose of this paper. To fully evaluate the accuracy that spaceborne three-line scanner can achieve, experiments with LMP, SECM and OIM triangulation algorithms are performed with a 500km length data sets under WGS 84 coordinate system. [full text]
-
. (2008) Photogrammetric Processing of Low Altitude Image Sequences by Unmanned Airship. In: ISPRS 2008 Congress, July 2008, Beijing, China. ISPRS, 37(B5): 751-758.

Abstract: Low altitude aerial image sequences have the advantages of high overlap, multi viewing and very high ground resolution. These kinds of images can be used in various applications that need high precision or fine texture. This paper mainly focuses on the photogrammetric processing of low altitude image sequences acquired by unmanned airship, which automatically flies according to the predefined flight routes under the controlment of autopilot system. The overlap and relative rotation parameters between two adjacent images are estimated by matching two images as a whole and then precisely determined by pyramid based image matching and relative orientation. The matched image points and ground control points are then used for aerial triangulation with collinearity equations. The aerial triangulated high resolution images can be used to obtain precise spatial information products, such as Digital Surface Model (DSM), Digital Ortho Map (DOM) large scale Digital Linear Graphic (DLG) and three-dimensional (3D) city model. Experimental results show that the developed remote sensing system is qualified for high overlap and high resolution stereo imagery acquisition. Moreover, the proposed approaches are effective for photogrammetric processing of low altitude image sequences, and have well potentials in large scale topographic mapping and precise 3D reconstruction areas. [full text]
-
, Quanye Du. (2008) Semiautomatic Extraction of 3D Curves Based on Snakes and Generalized Point Photogrammetry from Aerial imagery. In: ISPRS 2008 Congress, July 2008, Beijing, China. ISPRS, 37(B3): 731-734.
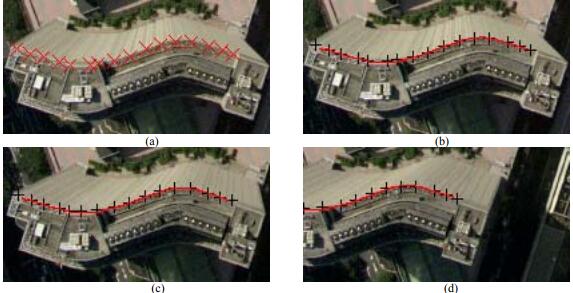
Abstract: The Snakes or active contour models of feature extraction algorithm integrates both photometric and geometric constraints. It derives the feature of interest by minimizing the total energy of Snakes with an initial location of the feature. Linear features can be directly processed with either x or y collinearity equation under the model of generalized point photogrammetry. In this paper, a new approach of extracting 3D curves based on Snakes and generalized point photogrammetry is proposed. Firstly, curve feature is extracted based on parametric B-spline approximation and Snakes on a single image. The seed points of curve feature on other images are determined by matching corresponding points. Then the corresponding curves are extracted by Snakes. Finally, the 3D curve model can be achieved by generalized point photogrammetry. Experimental results show that the proposed approach is feasible for 3D curve extraction. [full text]
-
, Hongchao Bing. (2005) Automatic Extraction of Tree Rows and Hedges by Data Integration Techniques. In: Proceedings of SPIE, November 2005, Wuhan, China. 6042 I.

Abstract: Data integration is a very important strategy to obtain optimum solutions in geo-scientific analysis, 3D scene modelling and visualization. This paper mainly focuses on the integration of GIS data, stereo aerial imagery and DSM to derive automatically tree rows and hedges in the open landscape. The roads, field boundaries, rivers and railways from GIS database also represent potential search areas for extracting tree rows and hedges, which are often located parallel and near to them. Different approaches, such as image segmentation by CIE L*a*b, edge extraction, linking, line grouping, space intersection and 3D verifying with DSM, are combined together to extract the objects of interest. The extracted information of tree rows and hedges can be used in many applications, such as deriving of wind erosion risk fields for soil monitoring and protection. [full text]
-
. (2004) Extraction Of Wind Erosion Obstacles By Integrating GIS-Data And Stereo Images. In: ISPRS 2004 Congress, July 2004, Istanbul, Turkey. ISPRS, 35(B3): 375-380.

Abstract: Data integration is a very important strategy to obtain optimum solutions in geo-scientific analysis, 3D scene modelling and visualization. This paper mainly focuses on the integration of GIS-data, stereo aerial imagery and DSM to derive automatically wind erosion obstacles in the open landscape to enhance the Digital Soil Science Map of Lower Saxony in Germany. The extracted wind erosion obstacles can be used to derive wind erosion risk fields for soil monitoring and preservation. GIS-data is used as prior information for the object extraction. The GIS-objects roads, field boundaries, rivers and railways from GIS database can represent initial search areas for extracting wind erosion obstacles, which are often located parallel and near to them. Wind erosion obstacles are divided in the semantic model into hedges and tree rows, because of different available information from the GIS-data, although their extraction strategies are similar. Different approaches, such as segmentation by NDVI and CIE L*a*b, edge extraction, linking, grouping and verifying with 3D information, are combined to extract the objects of interest. The extracted wind erosion obstacles are integrated into a semantic model, described by their 3D appearance in geometry, together with 2D elongated shadow regions in a known direction according to 3D information and sunshine. [full text]
-
. (2004) Measurement of Industrial Sheetmetal Parts with CAD-designed Data and Non-metric Image Sequence. In: ISPRS 2004 Congress, July 2004, Istanbul, Turkey. ISPRS, 35(B5): 640-645.
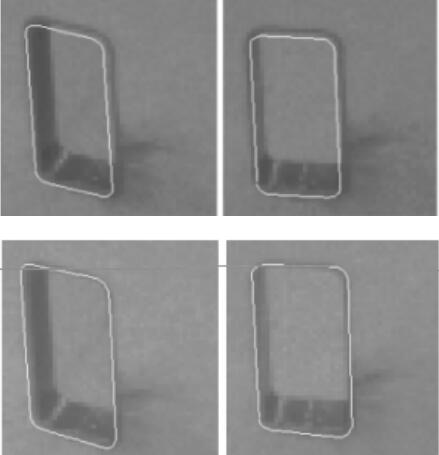
Abstract: A novel approach for three-dimensional reconstruction and measurement of industrial parts with CAD-designed data and non-metric image sequence is proposed. The purpose of our approach is to automatically reconstruct and thus measure the producing imprecision or deformations of industrial parts mainly composed of line segments and circles with information extracted from imagery. Non-metric image sequence and CAD-designed data are used as sources of information. Principles of 2D and 1D least squares template matching to extract precise lines and points are presented. Hybrid point-line photogrammetry is adopted to get accurate wire frame model of industrial parts. Circles, arcs and lines connected to each other on the part are reconstructed with direct object space solution according to known camera parameters. The reconstructed CAD model can be used for visual measurement. Experimental results of several parts are very satisfying, which shows that the proposed approach has a promising potential in automatic 3D reconstruction and measurement of widely existed industrial parts mainly composed of lines, circles, connected arcs and lines. [full text]
-
, Zuxun Zhang, Jianqing Zhang. (2003) 3D Reconstruction of Industrial Sheetmetal Parts with Hybrid Point-line Photogrammetry. In: Third International Symposium on Multispectral Image Processing and Pattern Recognition, October 2003, Beijing, China. 5286: 992-996.
Abstract: An approach for three-dimensional reconstruction of industrial parts with non-metric image sequence and hybrid point-line photogrammetry is proposed. Non-metric image sequence and CAD-designed data are used as source of information. The strategy of our approach is to reconstruct the parts automatically with points and line segments extracted from imagery. Hybrid point-line photogrammetry is used to reconstruct sheetmetal parts accurately, and the reconstructed model can be used for visualization and inspection. The reconstruction system can run automatically and fastly. The output of hybrid point-line photogrammetry is the final 3D geometric model of the part. Results of real images of several parts are very satisfying, which shows a promising potential in automatic 3D reconstruction of widely existed industrial parts mainly composed of points and lines. [full text]
-
, Zuxun Zhang, Jianqing Zhang. (2003) Photogrammetric Reconstruction of Arcs and Lines Based on one Dimensional Point Template Matching. In: 6th Conference on Optical 3D Measurement Techniques, September 2003, Zurich, Switzerland. pp. 315-321.
Abstract: For lots of pipe-like and board-like industrial parts, the reconstruction of circles, arcs and lines is very important but hard to deal with in practice. A new approach to match and reconstruct circles, arcs and lines based on one-dimensional point template matching technique and immediate object space solution is presented. Model of one-dimensional point template matching is addressed. Circles and arcs can be reconstructed easily and accurately with this model. Lines are represented by small segments. The length of small segments is approximately equal to that of point window in circle and arc reconstruction. Arcs and lines, which are connected to each other, can be reconstructed by an uniform solution with additional constraints. Results of experiment are satisfying. [full text]
-
, Zuxun Zhang, Jianqing Zhang. (2003) Orientation of Remote Sensing Image Pairs. In: 2003 Annual Conference of American Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, May 2003, Anchorage, USA. 0243.
Abstract: A new approach to obtain orientation parameters of remote sensing image pairs taken from different orbits by CCD line scanner is proposed. Mathematical model of obtaining orientation parameters by collinearity equations and coplanarity conditions is discussed. The traditional collinearity equations can be used for control point and its image correspondence, but it is not the case for non-control image correspondences. The two camera positions and the image correspondences should be coplanar and thus can be used to resolve the orientation parameters. In the cases of only a few ground control points available, the two models should be combined to get reliable orientation parameters. To combine the two models, space resection model of coplanar condition is modified. Algorithms of how to calculate the initial values of orientation parameters are also addressed. The proposed approach is tested with stereo image pair and results are given. [full text]
-
, Zuxun Zhang, Jianqing Zhang. (2003) Multi-view 3D City Model Generation with Image Sequences. In: 6th AGILE conference on Geographic Information Science, March 2003, Lyon, France.

Abstract: Rapid texture mapping of buildings and other man-made objects is a key aspect for reconstruction of 3D city landscapes. An effective approach by the way of coarse-to-fine 3D city model generation based on digital photogrammetric theory is proposed. Three image sequences, two oblique photography to buildings’ walls and one vertical photography to building’s roof, acquired by digital video camera on a helicopter, coarse 2D vector data of buildings and LIDAR data are used as sources of information. Automatic aerial triangulation technique for high overlapping image sequences is used to give initial values of camera parameters of each image. The correspondence between the space edge of building and its line feature in image sequences is determined with a coarse-to-fine strategy. Hybrid point-line photogrammetric technique is used for accurate reconstruction of buildings. Reconstructed buildings with fine textures superimposed on DSM and orthoimage are visualized realistically. [full text] [full text]
-
, Zuxun Zhang, Jianqing Zhang. (2003) Camera Calibration Technique with Planar Scenes. In: Proceedings of SPIE, January 2003, Santa Clara, USA. 5011: 291-296.
Abstract: A flexible new camera calibration technique using 2D-DLT and bundle adjustment with planar scenes is proposed in this paper. The equation of principal line under image coordinate system represented with 2D-DLT parameters is educed using the correspondence between collinearity equations and 2D-DLT. A novel algorithm to obtain the initial value of principal point is put forward in this paper. The practical decomposition algorithm of exterior parameters using initial values of principal point, focal length and 2D-DLT parameters is discussed elaborately. Planar-scene camera calibration algorithm with bundle adjustment is addressed. For the proposed technique, either the camera or the planar pattern can be moved freely, and the motion need not be known. Very good results have been obtained with real data calibration. The calibration result can be used in some high precision applications, such as reverse engineering and industrial inspection. [full text]
-
, Jingnan Liu, Zemin Wang. (2002) Errors Analysising on Combined GPS/GLONASS Positioning. In: 2002 International Symposium on GPS/GNSS, November 2003, Wuhan, China.
Abstract: This paper focuses on the major errors and their reduction approaches of combined GPS/GLONASS positioning. To determine the difference in the time reference systems, different receiver clock offsets are introduced with respect to GPS and GLONASS system time. A more desirable method of introducing a fifth receiver independent unknown parameter, which can be canceled out when forming difference measurements, is discussed. The error of orbit integration and the error of transformation parameters are addressed in detail. Results of numerical integration are given. To deal with the influence of ionospheric delay, a method of forming dual-frequency ionospheric free carrier phase measurements is detailed. [full text]
-
,Maoteng Zheng,Jin Yu,et al. (2012) On-orbit Calibration and Accuracy Evaluation of Three-line Scanner of ZY-3 Satellite. In: The First Symposium of High Resolution Earth Observation, December 2012, Beijing, China.
-
, Bo Wang, Jin Yu, et al. (2012) Automatic Generation of Advanced Geographic Products with Chinese Remote Sensing Satellite. In: 18th Remote Sensing Congress of China, October 2012, Wuhan, China.
Abstract: Satellite remote sensing is an advanced technology with abundant applications and great social benefits. This paper illustrated the key technologies and workflow of the fully automatic data processing system to process the ZY-02C and ZY-3 satellite imagery. Finally, the accuracies of geo-referencing and fully automatically generated advanced products, such as high-resolution color-fused image, digital elevation model (DEM), and digital orthophoto map (DOM), were discussed. [full text]